| Type |
|
| Engine |
|
| Dimensions |
|
| Weights |
|
| Performance |
|
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
|
|
|
|
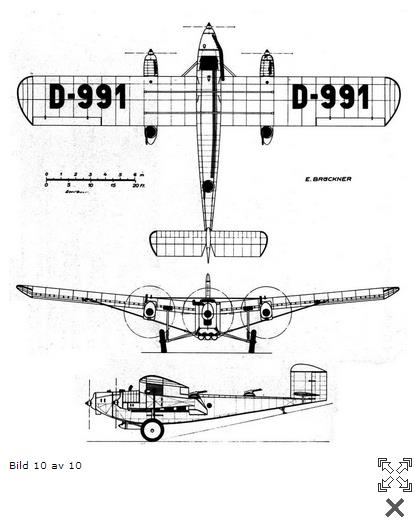
Ro XII, also listed as Ro VIII Mb, was the rebuilt Rohrbach Ro VIII Roland I c/n 18, D-991 which was returned to Rohrbach in August 1928 and was then converted to a bomber configuration. The airplane had been used by both Luft Hansa and Iberia.




In the course started in the mid 20s recovery was still secret German Air Force German industry should be established as well and bombers. As such "Immediate type weapons" - that sounded official designation, so it was proposed to develop a military version of a civilian aircraft firm Rohrbach «Roland». This aircraft, originally designated as Roland Mb, was not in the literal sense of the new design. It was a largely reworking previously received by the civil aviation machine, the oldest version of the sample.
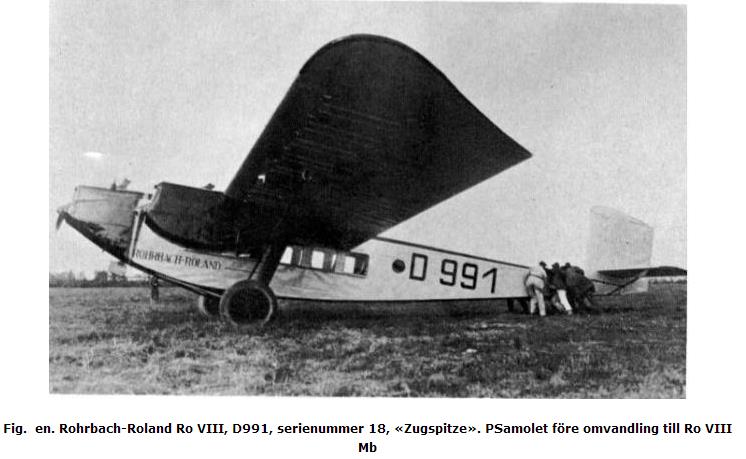
Fig. one. Rohrbach-Roland Ro VIII, D991, serial number 18, «Zugspitze». PSamolet before conversion into Ro VIII Mb
Although firm Rohrbach once repeatedly reported in the foreign press that the version of "Roland" was seen as a land or a night bomber, described its performance characteristics and weapons and even typical of the official designation of the military version of the aircraft («Mb»), in Germany for many years «Militär-Roland» remained almost unknown.
Was taken care of both the government and the Reichswehr with its aspirations to save the data of a secret. But on the other hand we must also take into account the fact that even before the 1933 is not very good for health was trying to look at the war maps or attempt to disclose them. It experienced the Walter Kreiser (Walter Kreiser), which is published in the journal «Weltbühne» some details about the mysteries of the German aviation industry and for this he was convicted by a court for betraying the country's interests. Situation was no better with the publisher of this magazine Carl von Ossiettski (Carl von Ossietzki) (Nobel Peace Prize 1936. Concluded at the end. Camp in 1938), which in this case was also sentenced to imprisonment. These draconian measures have led to the fact that further publications on this topic in the German press did not take place.
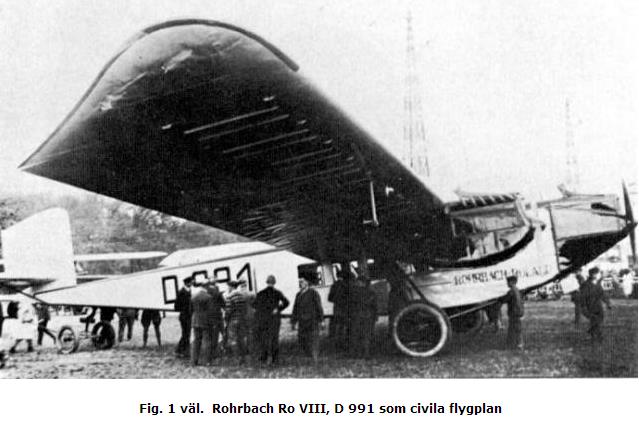
Fig. 1 well. Rohrbach Ro VIII, D 991 as a civil aircraft
Development
Before this sample was tested for use in war, he announced himself in civil aviation after the establishment of some world records (the first of the cars after the re-entry of Germany FAI). 4th February 1927 «Rohrbach-Roland» running Chief Pilot Shtayndorffa (Steindorff) in gusty wind and bad rainy weather despite the temporary stop and middle engine problems in the one of the outer engines performed successful flight. Thus were obtained the following parameters:
1. C payload of 100 kg: at a distance of 500 km was obtained speed 165.9 km / h (the previous record of 163 km / h).
2. Since the payload of 2000 kg:
2a. Flight duration 4 h 17 min and 49 (4 ca 4 min.)
2b. Flying in a circular route of 600 kilometers (500 miles).
2c. Speed at a distance of 100 km 173.9 km / h (150 km / h).
2d. Speed at a distance of 500 km 165.9 km / h (147 km / h).
Fig. 2. Rohrbach Ro VIII Mb board number 91 in Lipetsk. Even without defensive emplacements. Photo presumably in 1929. Left to right: unknown, engineer Prekel (Preckel) of the company Siemens, unknown engineer with the company Siemens, engineer Scholz (Scholz), adjuster Anlauff (Anlauff), unknown
Two months later, April 13, 1927, D991 during the flight route Mayland Munich for the first time crossed the Alps. The flight lasted 58 minutes 1:00 and from time to time at an altitude of 5200 prhodil meters. Return flight, which took place the next day, lasted 3 hours. Further experimental flights over the Alps in May 1927 also were successful. After which the aircraft began to make air traffic.
Held in the USSR for the test aircraft for the purpose of military applications, sootvetstsvii with conventional practice, the aircraft received other engines and propellers. In this case (as in the Junkers G 24) rings for mounting machine guns and equipment to clear the bombs were removed before the aircraft flew along the route Konigsberg Dunaburg - Moscow and further to Lipetsk. When installing on-board weapons Roland Mb aircraft manufacturer Rohrbach metal (Rohrbach Metall-Flugzeugbau GmbH - RMF) based on the experience gained in the implementation of earlier foreign orders. As airborne weapons was provided old gun MG 08/15 with a special shoulder rest, which was supplied to the aircraft turrets Siemens-Schuckert.
In Lipetsk, located about 300 km south of Moscow, was then known as the Scientific Test Center aircraft (abbreviated Wivupal. This designation had several meanings. For example: "Scientific research and training camp for training.") Aircraft here snachala completely retrofitted and were then tested in flights referents armament Wa Prüf 8. After the technical inspection of the aircraft followed to check the possibility of using this aircraft in the Air Force. In this case, the aircraft company Rohrbach became only the "second winner". Preference was given to 24 G, whose equipment was simpler and therefore give less bounce.
Fig. 3. Rohrbach Ro VIII Mb in Lipetsk on tests with three bombs under the fuselage
«Militär-Roland» had a simple mechanical system reset bombs (described in a scientific paper Rohrbach number 21). Located near the site scorer drive levers were associated with the release gear by ropes. Release gear depending on the caliber of the carried bombs were operated individually or in groups. Maximum bomb load was 1100 kg (according to other sources to 1000 kg). Usually it would be 50 kg or 300 kg of explosive bombs PuW.
To select whether to reset the bombs carried out using elekticheskih sensors. Each bomb or bombs could be dropped group in sequence or combination. Reset implemented mechanically by a single lever within the cab scorer, which was and bombsight. The manual there as well elektpicheskoe warning placards provide information about the status of each bomb. Ie prepared if a bomb to be reset by selecting whether to reset or reset. Bombs hung on ropes in external underwing or ventral suspension. While the device itself to reset the bombs were assembled inside.
In cases where the bomber was used temporarily as a scout on the bomb racks located under the wings could hang suspended large tanks. The aircraft is equipped with cameras and communications.
In the first embodiment of the auxiliary 2 bomber bomb racks for 300 kg bombs under the wings were attached, while ten bomb racks designed for hanging 50 kg bombs rasplagalis fuselage. Five of them were in the bottom of the recess of the fuselage. At these points in the fuselage bomb suspension were suspended in flight using moving the cart after the first five bombs were dropped. But there was also a significant disadvantage because moving and fixing bombs lasted more than a quarter of an hour - too long a gap, in the MDM plane was circling in the area raspolozheniya purpose.
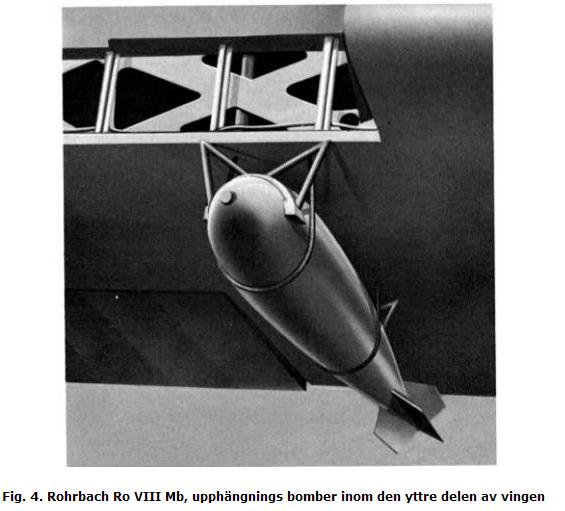
Fig. 4. Rohrbach Ro VIII Mb, suspension bombs under the outer part of the wing
Applied in «Militär-Roland» bombs suspension system was beneficial in terms of aerodynamics. But on the other hand does not fully meet the demands placed upon it. Mount hanging on the ropes bombs required a lot of time and also required for large bombs hanging under the wings of almost three meters above ground level, setting up special podorevatelya. So the military demanded promptly equipping aircraft more suitable for these purposes means for bomb release.
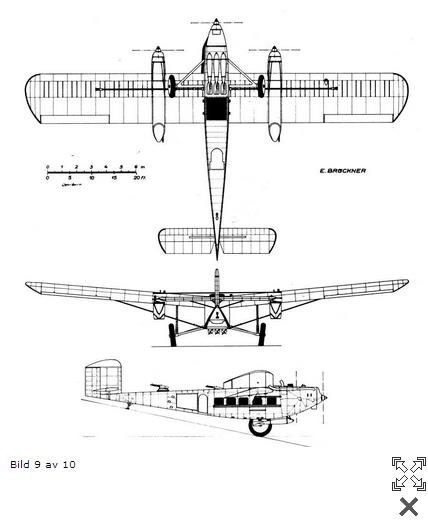
Taking the night bomber version (four machine guns, of which at least one in the bottom of the fuselage in front of the closed circular fairing at the rear having an elongated rectangular cut), Rohrbach company hoped to strengthen and improve the armament sector shelling thus creating an acceptable Daily bomber. In addition to the top of the fuselage firing point, similar to the French and American Bleriot 117 Curtiss Condor, in elongated pods on the wings engines were placed two cabins with machine-gun fire points. Blagadaryu this plane got firepower 3 times greater than that of the G 24. Especially in the rearwardly downward, but its maximum load at this bomb dropped to 800 kg. Between the two motor gondolas through the upper part of the fuselage were about 2-pull parallel tether.
In 1928, he was determined following the test plan Roland Mb: to July 23, 1928 bomb test group (Versuchsgruppe Bomben) had to concentrate in the area of testing (Lipetsk). Preparation of the test section, conducting classes and other bombing completed by August 1, 1928. In the period from 1 to 21 August 1928 A 35 aircraft, G 24 and Rohrbach Roland Mb reworked and made tentative drop bombs with 35 A (according to other sources Ro VII was converted in Germany, perhaps, the term refers to remake dismantled before mounting overtake equipment ).
Fig. 5. Rohrbach RoVIII Mb, D-991, with its hanging bombs, machine-gun fire points in elongated pods and firing point at the rear underside of the fuselage. You may notice the back of the bombs in the mine for their discharge in the fuselage
10 starts with 40 bombs dumped training with Roland Mb (and an equal number of starts and bombs dropped from G 24) were to be held August 22 and September 15, 1928. Reset combat bombs (24 pcs. In two starts) were provided for Roland Mb between September 16 and October 15, 1928. Before that were produced 8 more starts with 100 A dumped with 35 bombs.
The aim of this work for later in 1929 was the end of term program of weapons. This included the establishment of the final equipment of both aircraft types have been tested according urgent weapons program, - Roland Mb and G 24 bomber with equipment and iron sights. Dropped bombs weighing 300 kg and 12.50 with the applicable fuses with them, Bomber equipment and sights.
In April 1929, a meeting was held on the future development of the bombing equipment and the purchase of all items for Roland Mb. Device provided for summer 1929 tests were collected and forwarded to the place of testing. Fitted bomber equipment and machine guns Rohrbach D991 flew to Lipetsk 15 June 1929. The next day, he was followed by G 24 (serial number G 878).
After comparison with the first two aircraft G 24 showed their advantages by Rohrbach, steps were taken to improve the aerodynamics and performance «Militär-Roland». When he was introduced this year for the second time, the shape of the firing points and points of engine mounts were a little ennobled. System has been changed and modified landing gear arrangement of suspended bombs. New, approximately 50 cm higher gear, allowed to place on the ventral suspension 300 kg bombs. Previously located in the fuselage holders 10 50 kg bombs were placed in groups under the wing panels. Each of the groups was calculated by 5 bombs.
In addition, and original ways suspension bomb load and had a third. This method is available to the documents not disclosed, but the information about it is available on a single photo. It lacks suspension for mounting bombs under the wings of three 300 kg bombs PuW suspended under the fuselage, 50 kg PuW bomb fastened behind them in the fuselage as in the original version.
When produced in the 1929 tests were first used electromechanical equipment for bomb release firm Rohrbach, which enables to perform a selective reset them each individually bombs. In these tests, again having problems and for this reason the test was interrupted. While during further tests used equipment company Siemens, which also provided for use on Roland Mb. For installation on the aircraft hangers to accommodate 50 kg bombs was necessary to make stronger individual sections of some of the ribs of the wing.
Regarding these attempts and second on the basis of the experience gained, it was concluded that in future aircraft manufacturing firms in these samples only aircraft had the right to apply their own sets of weapons for carriages, machine guns and mounts relief devices bombs, but that would be united - and comes to standardized specialized firms classified as "weapons."
Installation of equipment from Siemens as on Roland Mb meant began to apply the device to reset the bombs only a single type - for urgent variant weapons - it was the beginning of the late standardization in this area.
The results of this work, especially the experience gained in the summer of 1929 were set out in the conclusion of IIb (not preserved). Testing auxiliary bomber was zaversheno in late 1929, with «Militär-Roland» prototype and its competitor G 24 (which is interesting as well, and M 20) were found to be relatively relevant presented for their business requirements. In other words, their machine-gun Blagadaryu weapons and bombs were previously civilian aircraft, they are in any case were not full-fledged combat vehicles, but rather a sheep in wolf's clothing. Trimotor Roland Mb and G 24 were not well suited for the tasks that were set before them. Fuselage due to an engine mounted in front of him, do not let there be positioned scorer and defensive weaponry, because of the lack of the normal review scorer had to use the periscope type Goerz Fl 218 as a bombsight.
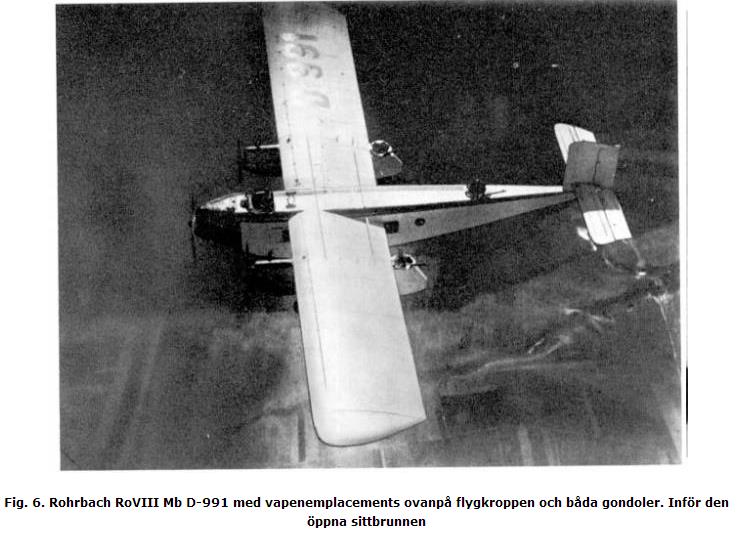
Fig. 6. Rohrbach RoVIII Mb D-991 with gun emplacements on top of the fuselage and both nacelles. Ahead of the open cockpit
As a result, various modifications and alterations that have undergone is not quite true Roland, the aircraft became too unwieldy. Pilots evaluated it is not particularly high. The maximum height of its flight at full load (4.5 km) from the point of view of the vulnerability of antiaircraft fire and flight speed were at a significantly lower level than that of other military aircraft of the time (for example Fokker CV 1928).
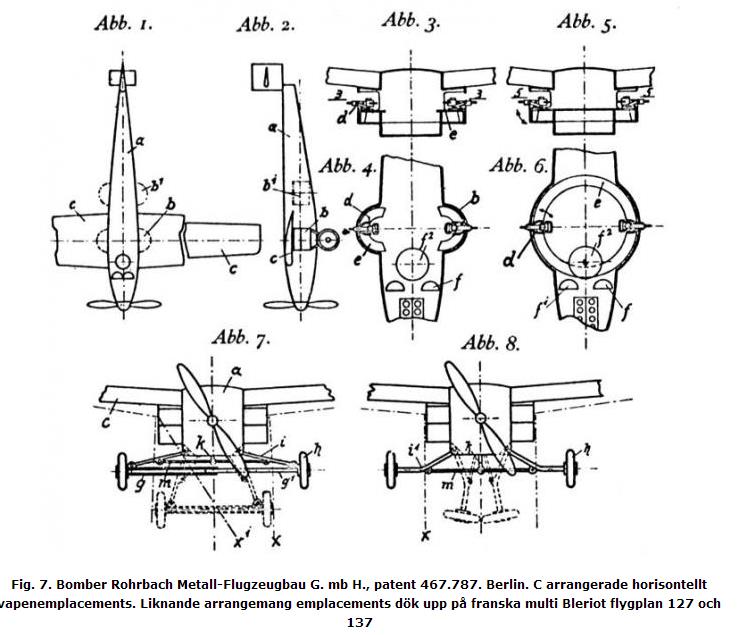
Company Rohrbach these shortcomings machines were known and it has taken steps to address them. Patent DRP 476 787 (registered 17.01.1929 year, received confirmation of registration 08.05.1929 year) company tried to protect the new plane (by location) mobile gun emplacements. Pat provided accommodation emplacements on both sides of the fuselage as balconies optimal in terms of aerodynamics shape.
In order to increase the sector shelling machine equipped so it was necessary to move the chassis and concentrate them at the center of the fuselage. Why instead did not include retractable landing gear, which at the time although it is rarely used, but is nevertheless the latest technology and do not require the high cost of implementation, it is not clear.
Today seem unacceptable graceful emplacements were for the then looks not so absurd. This arrangement emplacements could not be applied in practice by Rohrbach (not due to other technical reasons), but came up again a few years later in 1932 in a somewhat modified form in French Bleriot 137 bomber, whose predecessor had emplacements similar to those were at Roland Mb. And, presumably for the same reason, has the same problem. Bleriot 137 reminds project by Rohrbach appearance and location of the wing. Patented by Rohrbach and his French opponent emplacements became the initial sample for later applied to American combat aircraft emplacements blister.
According to other sources such changes supposedly got only one Roland Mb. There is one picture, which you can see on the upper side of the wing inscription D-991, while the fuselage there are no markings. Until now, it is believed that for these purposes has been redesigned aircraft with serial number 18. However, according to the results of the research have any doubts on this score.
Fig. 7. Bomber Rohrbach Metall-Flugzeugbau G. mb H., patent 467,787. Berlin. C horizontally arranged gun emplacements. Similar arrangement emplacements appeared on French multi Bleriot aircraft 127 and 137
D-991 with serial number 18 and the symbol Ro VIII disappeared in April 1928 from the machines used on scheduled flights "in connection with the operation abroad." In July of the same year he reappeared in the column "Change" under the new designation Ro Vlllb owned and test center in DVL Adlerhofe!
Founded in 1927, the Spanish airline IBERIA December 14, 1927, organized jointly with the German paptnerami flights on the Madrid-Barcelona using purchased in Germany trimotor type Rohrbach Roland. We are talking about D-991 (Spanish designation first M-Szasz, later M-CAAC), D-999 (M-SVVV), D-1124 (M-CCCC). So, check for D991 as the aircraft for air was somewhat belated.
According to these data the Spanish airline IBERIA 3 aircraft used until its liquidation in 1929, that is not quite true, because one of these aircraft in March 1928 in Muniesa near Teruel in fog collided with the ground and was completely destroyed (3 injured) . Image of one of the photographs that we are talking about the former CAAC or D-991. If we recall that another car may D-999 was returned to Germany and eventually was converted into an auxiliary bomber available in Spain since the beginning of 1928 was supposed to be only one Roland to perform flights. But in this case IBERIA had 2 other Rohrbach Roland D-1280 «Feldberg» RoVIII, serial number 35. Spanish designation M-SAEE and D-1338 «Zugspitze» Ro VIIIa, serial number 40, the Spanish designation M-CADD. So that when the subsequent nationalization in 1929 the company actually had three machine types Roland, even if it were not transferred from the first 3 cars the shipment.
Is the D-999 or, according to other sources, D-1280 was given back to the Germans, or vice versa designation D-991 applied for recognition of complications - is still not well defined. During trials in Lipetsk on the fuselage and wing of the plane were the digits 91. When you stretch the contrary - D 991 or D-991. Its exact name as before is not a known. In most firmehe prototype was designated Mb, at Siemens - Ro 2, as well as R 2. On the other had, Parties and designation Ro-XII "RoKa". On the fate of the auxiliary bomber that is based on Roland-converted and there is no accurate data. According to unconfirmed data plane English D991 running pilot hornless Hans (Hans Komoll) somewhere in the 1930 - 31 years was distilled in Germany (Berlin / Heerstrasse) conversion and as a result of the accident was completely destroyed. According to others the aircraft until 1945 was at the entrance to the aviation museum in Berlin Leterrier Bahnhof (Lehrter Bahnhof).
Brief description of Ro VIII Mb.
Purpose: Military aircraft (night, day bomber later) Crew: 4 (night bomber) Armament: 4 machine guns (night bomber) Arrangement of Wing: vysokoplan
Fuselage
Fuselage quadrangular with strongly rounded upper edges. Possessed good visibility cockpit with two seats positioned close set back and is located on top of the fuselage in front of the front edge of the wing. In the middle of a large lounge for 10 passengers. Entrance door to him at the right side. Behind the passenger compartment is a special compartment, access to which is carried outside through a large hatch (usually used to transport luggage). Melallicheskaya fuselage design of smooth duralumin with simple profiles. Two are located in the area of the middle compartment of the frame have a special gain in the attachment to the wing. Placed on the outside of the flanges of the frames over their entire length are connected with the outer skin. In the corners of a fuselage powerful riveted with the outer skin of the farm.
Power plant
The power plant consists of three 240-horsepower water-cooled engines BMW IV total capacity of 720 hp Average nosovoy engine located in the fuselage, two engines - in special pods located under the wing. Fuel tanks located in the wing. Drive diaphragm pumps, radiators engines could be carried out with the pilot's seat with the help of pin valves.
Carrier planes
The wing cantilever consisting of three parts, distributed along the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. Both wing with rectangular cross-section and the specially rounded outer extremities of the bent V-shaped with an angle of 6 ° with respect to the middle part. Dural cavity serve to accommodate the chassis. Much less prominent bow and stern landing gear closed by levers. Inner Wing flaps in open niches for legkodostupna service (invention firm Rohrbach). A portion of this recess is adapted to accommodate the fuel tank.
Designed as beam braces go from the middle of the wings to the fuselage bottom.
Empennage
Empennage performed as well as carrier planes with easy access to the interior. Unbalanced rudder. Large vertical tail size dyal good controllability of the aircraft in case of failure of one of the engines installed in the wing.
Chassis
Each of three droplet landing gear made of steel tubing supports the wheel (1250 × 250 mm, steel wheels with spokes). Two of these struts, which are being sucked, arranged horizontally. Rear of the rack supporting the rear wheel was zakreplena on the bottom of the fuselage on a flexible crutch. The third vertical strut supports the wheel opposite the corresponding increase in the part of the wing. It consisted of a strut with helical springs without prestressing. Chassis ensure a soft landing and short run as well and at a high speed (100 km / h).
Equipment
Radio with antenna Max load capacity of 70 watts. Generator driven by an air flow, 12 volt battery, fire extinguisher, gyro attitude indicator, altimeter special for night flights. Searchlight
Technical data Rohrbach Ro VIII Mb
Wingspan: 26000 mm Length: 16300 mm Height: 5100 mm Elongation fuselage: 1: 7.7 Wing Area: 88m ² Powerplant: three 240silnyh BMW IV engine with a total capacity of 720 hp Weight (without water cooling system ): 4050 kg Payload weight: 2550 kg All normal takeoff: 6600 kg Specific wing loading: 75 kg / m ² Specific load capacity: 9.2 kg / hp. Armament: 4 machine gun MG 08/15 Crew: 4 Human Maximum speed: 198 km / h Service ceiling: 5600 m









