| Type |
Single seat fighter |
| Engine |
1 Junkers Jumo 004B |
| Dimensions |
Length 9,25 m , height , span 8,2 m , wing area , |
| Weights |
Empty , loaded , max. take off weight |
| Performance |
Max.. speed 840 km/h, cruising speed , range , endurance , service ceiling , climb |
| Armament |
2 MK 108 30mm cannon in the fuselage nose and 2 MG 151/20 20mm or 2 MG 151/15 cannon in the wing roots. |
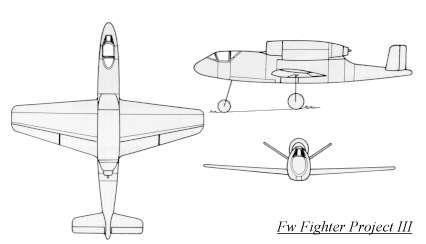
Continuing the Focke-Wulf early jet fighter designs, the P.III is also known as the P.II (dated December 22, 1942) in some references. It had a straight wing with a more pronounced taper on the trailing wing edge than the leading wing edge. The jet engine was located on top of the fuselage just behind the cockpit (like the Heinkel 162), and exhausted over the V-tail. A tricycle undercarriage was fitted and the armament consisted of two MK 108 30mm cannon and either two MG 151/15 15mm machine guns or two MG 151/20 20mm cannon.
The Focke-Wulf Project III was a design study for a jet fighter, carried out in Germany in June 1943. It aimed to reduce the risk of foreign object damage to the engine that had been foreseen for the Project II, by relocating the engine from beneath the fuselage to a position atop the fuselage, with the jet intakes at the fuselage sides. In most other respects, it was similar to Project II, but as well as the engine relocation, Project II's conventional tail was replaced with twin tails on the ends of the horizontal stabiliser, in order to provide a path for the jet exhaust.