| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
|
|
JK+ |
|
|
|
CD+SE |
|
|
|
DW+TU |
|
|
|
DW+TV |
|
|
|
DW+UT |
FFS A/B 52 |
| Type |
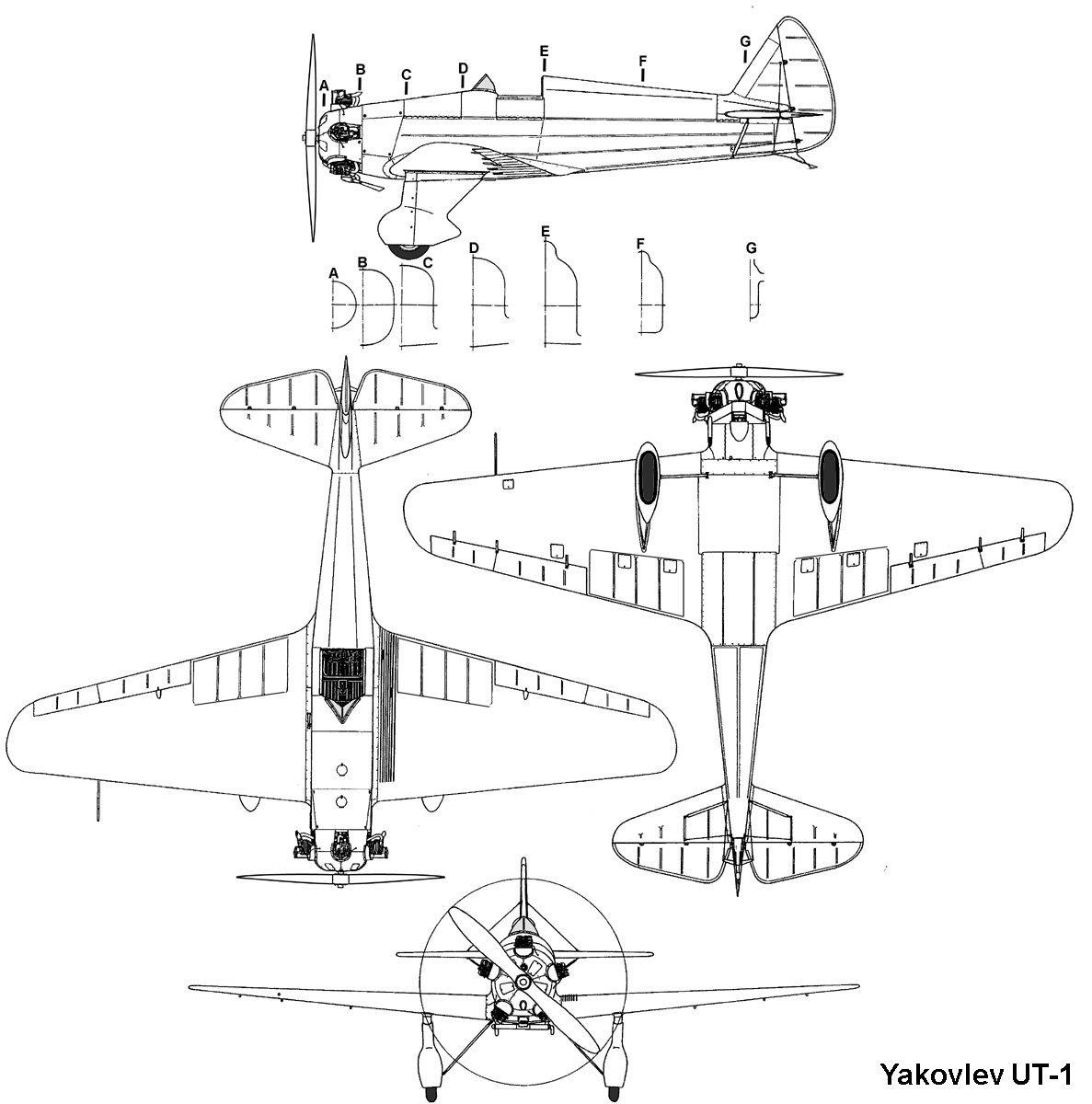
Single seat trainer |
| Engine |
1 Shvetsov M-11Ye |
| Dimensions |
Length 5,75 m , height 2,34 m, span 7,3 m , wing area 9,58 m2 , |
| Weights |
Empty 429 kg, loaded 597,5 kg , max. take off weight |
| Performance |
Max.. speed 257 km/h , cruising speed , range 670 km, endurance , service ceiling 7120 m , climb 7,4 m/sec. |
Compact monoplane aerobatic trainer with open cockpit. When the I-16 fighter came to service, it became obvious than biplane trainers (like U-2) do not provide enough training ground to fly fast and 'hot' monoplane fighters. A.S.Yakovlev was one of the first designers who started to built monoplane trainers to match I-16 performance.
AIR-14 construction was similar to this of AIR-10: wire-braced fuselage of wielded soft steel tubes, with light wooden structure supporting the skin and providing the clean shape to the fuselage. Wing - single-piece with two spars, converging toward the wingtip (later this construction was used in Yak-1). Tailplane, tailfin and ailerons had aluminum frame. All skinning - fabric. Landing gear - fixed with rubber shocks. To prove its reliability Yu.I.Piontkovsky performed 300 landings during single day, followed by 1000 more (in few days).
State Acceptance Trials took place in 1936 with 100hp M-11. After minor modification and installation of 115hp M-11G aircraft was presented again in 1937 and after successful trials production was launched. Later with 150hp M-11E performance was improved again. In 1939 engine cradle was extended forward, making handling easier. Same modification included new fuel system, allowing inverted flight. Small series were built with oleo-pneumatic shocks and single machine-gun.
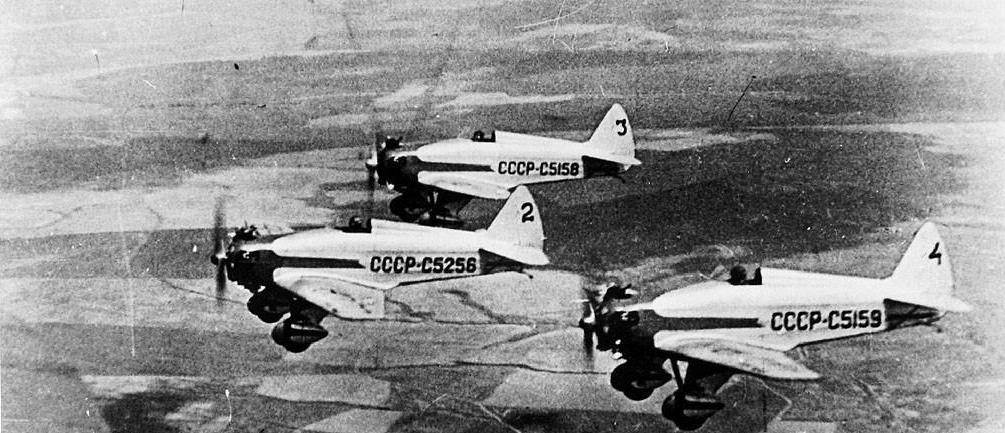
In 1937 UT-1 was installed on floats, setting two records in October same year: October 2: Yu.I.Piontkovsky set speed record 218km/h at 100km; October 21: D.N.Fedoseev flew floatplane from Moscow to Ufa, covering 1174km non-stop;
Total number of variants was about 10, with different wing section, new propellers, floating ailerons etc. Not all of them were successful.
UT-1 was too demanding for primary trainer, and biplanes were still used on early training stages.
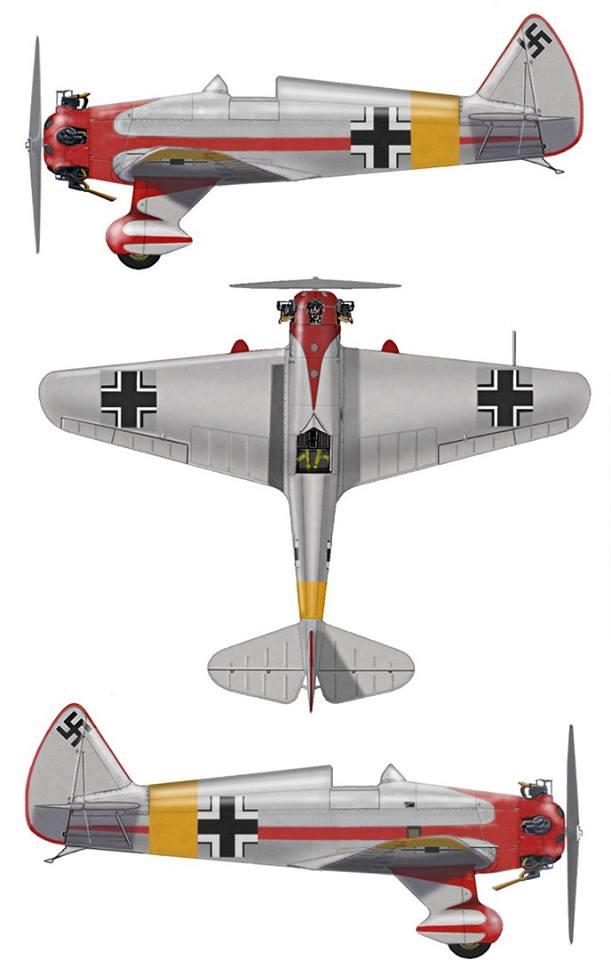
In 1941 some UT-1s were armed in frontline workshops. Typical armament included two ShKAS machineguns and few RS-82 rockets under the wings.
1241 built in 1937-1940. UT-1 established eight international records of speed, ceiling and range. Light trainer remained unsurpassed as aerobatic/sport aircraft until 50's.