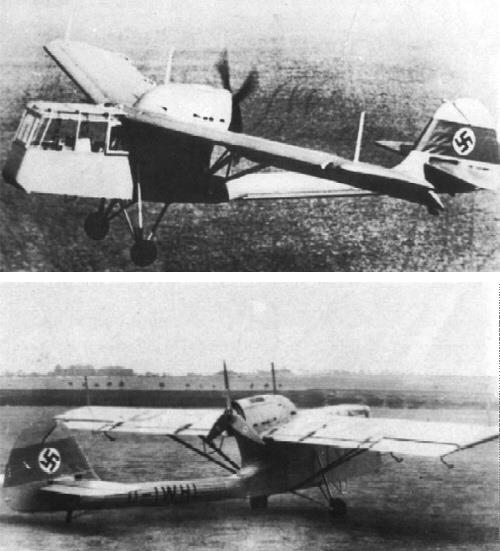
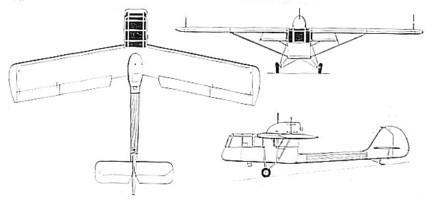
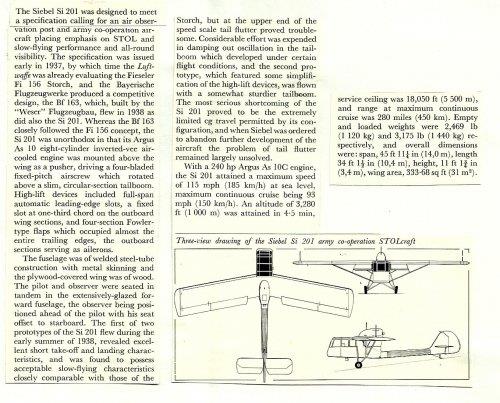
The Siebel Si 201 was designed to meet a specification calling for an air observation post and army co-operation aircraft placing emphasis on STOL and slow-flying performance and all-round visibility. The specification was issued early in 1937, by which time the Luftwaffe was already evaluating the Fieseler Fi 156 Storch, and the Bayerische Flugzeugwerke produced a competitive design, the Bf 163, which, built by the "Weser" Flugzeugbau, flew in 1938 as did also the Si 201. Whereas the Bf 163 closely followed the Fi 156 concept, the Si 201 was unorthodox in that its Argus As 10 eight-cylinder nverted-vee aircooled engine was mounted above the wing as a pusher, driving a four-bladed fixed-pitch airscrew which rotated above a slim, circular-section tailboom. High-lift devices included full-span automatic leading-edge slots, a fixed slot at one-third chord on the outboard wing sections, and four-section Fowlertype flaps which occupied almost the entire trailing edges, the outboard sections serving as ailerons.The fuselage was of welded steel-tube construction with metal skinning and the plywood-covered wing was of wood. The pilot and observer were seated in tandem in the extensively-glazed forward fuselage, the observer being positioned ahead of the pilot with his seat offset to starboard. The first of two prototypes of the Si 201 flew during the early summer of 1938, revealed excellent short take-off and landing characteristics, and was found to possess acceptable slow-flying characteristics closely comparable with those of the Storch, but at the upper end of the speed scale tail flutter proved troublesome. Considerable effort was expended in damping out oscillation in the tailboom which developed under certain flight conditions, and the second prototype, which featured some simplification of the high-lift devices, was flown with a somewhat sturdier tailboom. The most serious shortcoming of the Si 201 proved to be the extremely limited cg travel permitted by its configuration, and when Siebel was ordered to abandon further development of the aircraft the problem of tail flutter remained largely unsolved.
i
| Type |
V1 |
V2 |
| Engine |
1 Argus As 10C with 4-bladed propeller |
1 Argus As 10C with 3-bladed propeller |
| Dimensions |
Length 10.4 m, height 3.4 m, span 14.0 m, wingarea 31 m2 |
| Weights |
Empty 1120 kg, loaded 1440 kg , max. take off weight |
| Performance |
Max. speed 185 km/h at sea level, max. cont. cruising speed 150 km/h, time to 3000 m 4.5 min, service ceiling 5500 m, range at max. cont. cruise 450 km , landing speed 50 km/h, starting run 245 m, landing run 160 m, endurance 3 h |
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
| V-1 |
|
D-IYVN |
First flight 30th of July 1937, pilot Flugkapitän Ziese |
| V-2 |
|
D-IWHL |
Minor change on the wings |