Civil Registration of the eight built
ES-ASN PTO-4
ES-CFI PTO-4
ES-EAK PTO-4 Eesti Aeroklubi 00.00.38
ES-EAL PTO-4 Eesti Aeroklubi 00.00.38
ES-EAM PTO-4 Eesti Aeroklubi 00.00.38
ES-EAN PTO-4 Eesti Aeroklubi 00.00.38
ES-EAO PTO-4 Eesti Aeroklubi 00.00.38
ES-EAP PTO-4 Eesti Aeroklubi 00.00.38
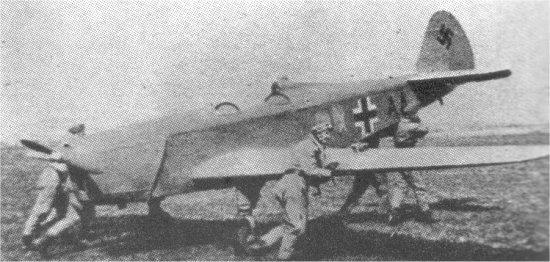
In 1938, the Estonian aviation engineers Voldemar Post, Rein Tooma and Otto Org, previously responsible for the PON-1 trainer, designed and built the PTO-4 training aircraft. It was a two-seat low-winged monoplane powered by a De Havilland Gypsy of 120 hp, with a fixed undercarriage that could be fitted with wheels or skis. The aircraft could fly at a maximum speed of 245 km per hour and had a ceiling of 5,000 meters. On 12 October 1938, the PTO-4 was taken into service of the Air Force.
The Estonian Air Force received two PTO-4s (serial numbers 161 and 162), one with an open cockpit and the other an enclosed cockpit. Six examples were in civil use, of which five were used by the Eesti Aeroklubi (EAK), a flying club controlled by the Estonian Military.
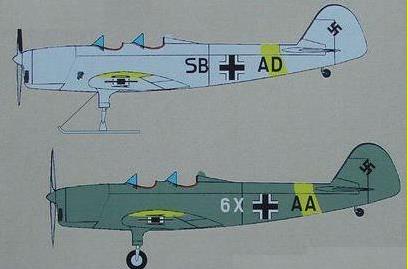
Four examples surviving from the Soviet occupation of Estonia (1940-41) were operated by the German Luftwaffe, being operated by a unit manned by Estonian volunteers (initially called Sonderstaffel Buschmann and later 1./SAGr.127) based at Reval-Ülemiste airfield. They were operated as training and liaison aircraft as well for coastal patrol over the shores of the Baltic.
| Type |
2-seat trainer |
| Engine |
1 De Havilland Gipsy Major |
| Dimensions |
Length , height , span , wing area , |
| Weights |
Empty , loaded , max. take off weight |
| Performance |
Max.. speed 245 km/h , cruising speed , range , endurance , service ceiling 5000 m , climb |
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
|
|
SB+AA |
Gruppe Buschmann |
|
|
SB+AB |
Gruppe Buschmann |
|
|
SB+AC |
Gruppe Buschmann |
|
|
SB+AD |
Gruppe Buschmann |