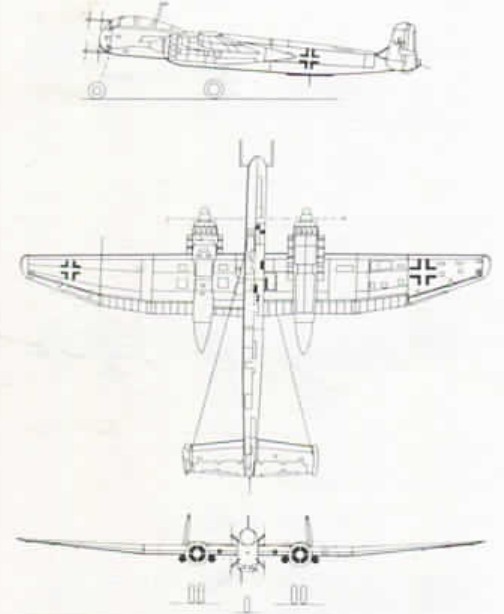
| Type |
Two seat nightfighter |
| Engine |
|
| Dimensions |
Length , height , span , wing area , |
| Weights |
Empty , loaded , max. take off weight |
| Performance |
Max.. speed , cruising speed , range , endurance , service ceiling , climb |
| Armament |
|
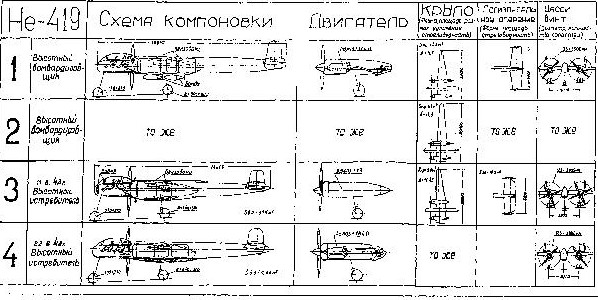
Since the He 219 A could only reach a summit height of 9200 m. The higher version B did not make it, the Me 419 was developed as a high altitude fighter in 1943 from the He 219 using many parts of the 219.
The work progressed slowly in Januari 1943. and for this was the use of numerous parts of the He 219 A. So the fuselage and the control unit for the were used He 419, the He 419
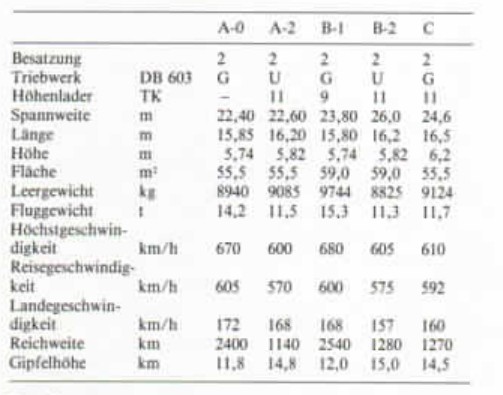
He 419 A-0 from a typical He 219 A-5 This would then lead to the DB 603G, a significant increase in the size of the DB 601. The new G-variant would have an output of 2000 hp, with the wings being overhauled and a span of 22.40 in length. Wings modified and tail section changed This is planned for the He 419 B-1/R 1 This would be one had to fall back on the power of the 319, which was to be enlarged again, now to 23.000 hp. The DB 603G engines were to be completely replaced in their positions by high-altitude superchargers. As for the armament, one thought was to have MG 151/20 in the wing roots and four Mk 108 under the fuselage. The machine, , would have been able to reach 2 km/h in 15 minutes at an altitude of 14,500 m. The maximum speed of the first model was 670 km/h at a weight of 14 200 kg. The cruising speed 650 km/h, die landing speed
172 km/h. 2400 km range