| Type |
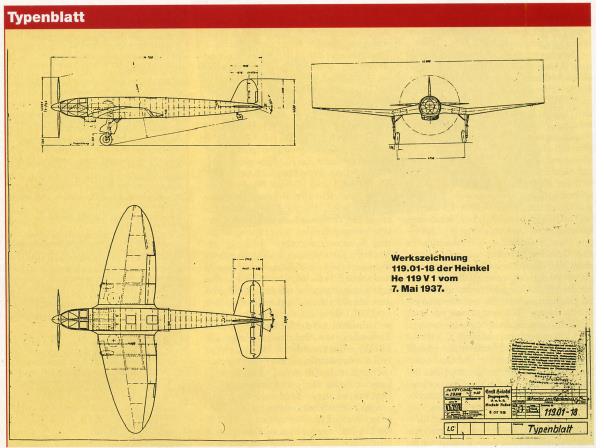
V1 3-seat experimental |
V3 3-seat sea plane |
| Engine |
1 Daimler-Benz DB 606Aa |
1 Daimler-Benz DB 606Aa |
| Dimensions |
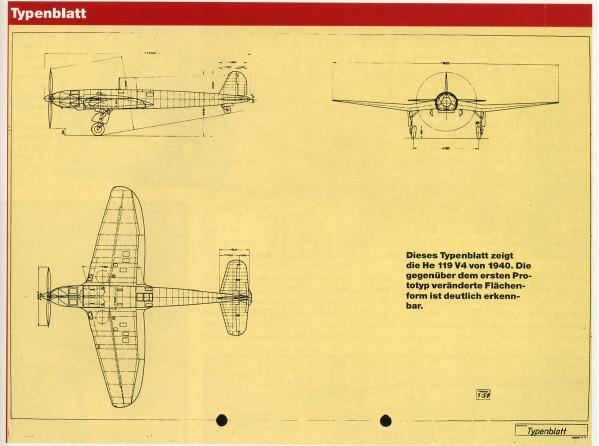
Length 14,8 m, height 5,4 m , span 16,0 m , wing area 51,6 m2 , |
|
| Weights |
Empty 5120 kg, loaded 8100 kg , max. take off weight , fuel 1750 kg |
|
| Performance |
Max.. speed 485 km/h at sea level, 585 km/h at 4500 m, cruising speed 490 km/h at 4500 m , landing speed 120 km/h, range 2000 km , endurance , service ceiling 8500 m , climb to 2000 m 3,2 min., to 4000 m 6,5 min. |
|
| Armament |
None |
|
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
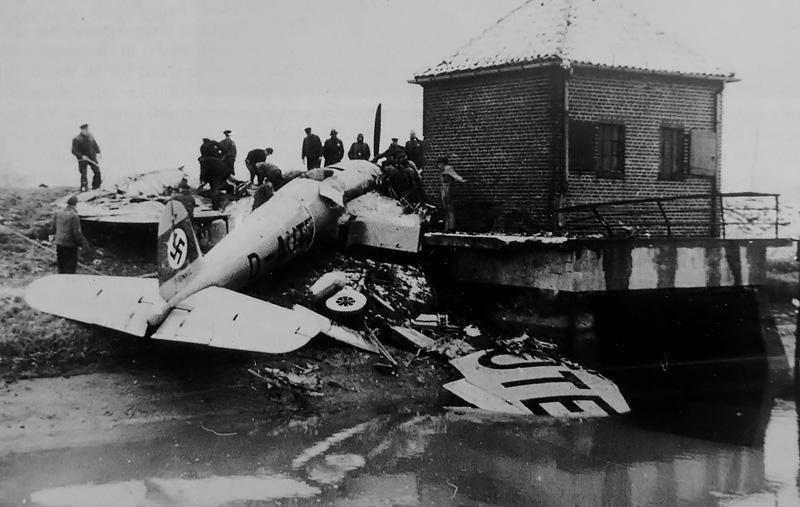
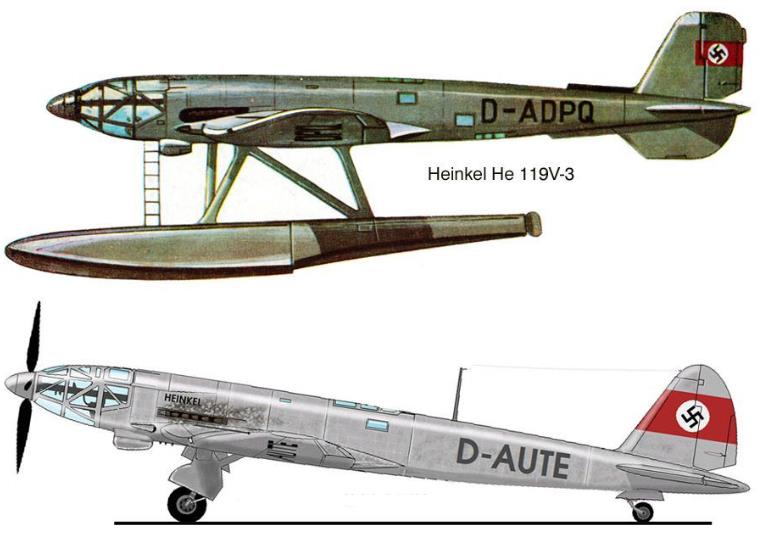
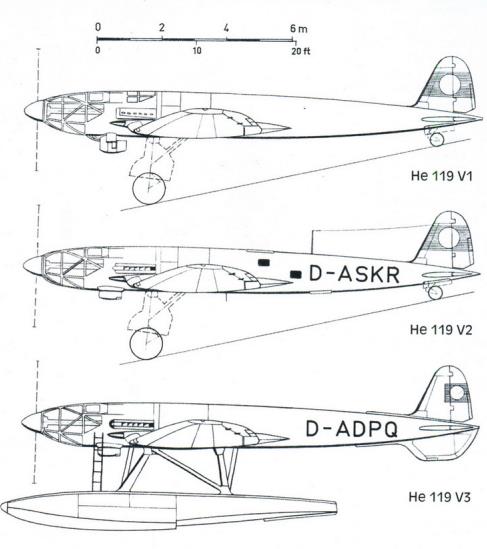
| V1, SV-1 |
2402 |
D-AUTE |
Crashed 1938 |
| V2, SV-2 |
2403 |
D-ASKR |
First flight September 1937. Delivered to Japan 1941, soon after delivery it was damaged |
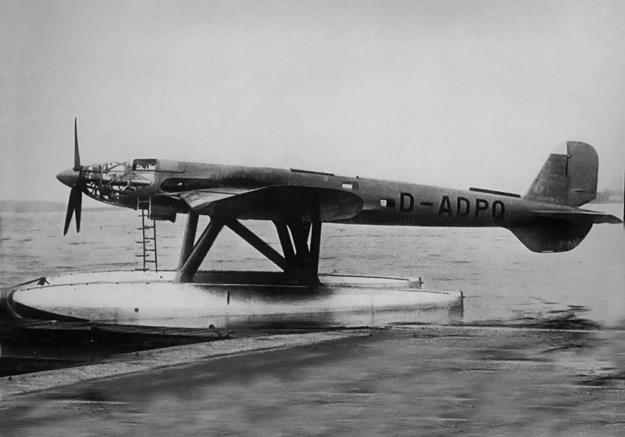
| V3, SV-3 |
2404 |
D-ADPQ, BB+DR |
Sea plane. First flight 7.10.1938. Delivered to E-Stelle Travemünde In March 1941 to the Deutsche Luftfahrtsammlung |
| V4 |
2405 |
|
First flight in May 1940. Delivered to Japan 1941, soon after delivery it was damaged |
| V5 |
|
|
Source "Green". Reconnaissance. Probably wrong |
| V6 |
|
|
Source "Green". Reconnaissance. Probably wrong |
| V7 |
|
|
Source "Green". Bomber. Probably wrong |
| V8 |
|
|
Source "Green". Bomber. Probably wrong |
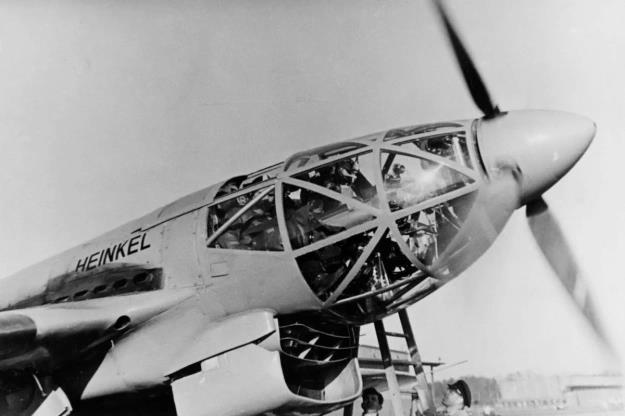
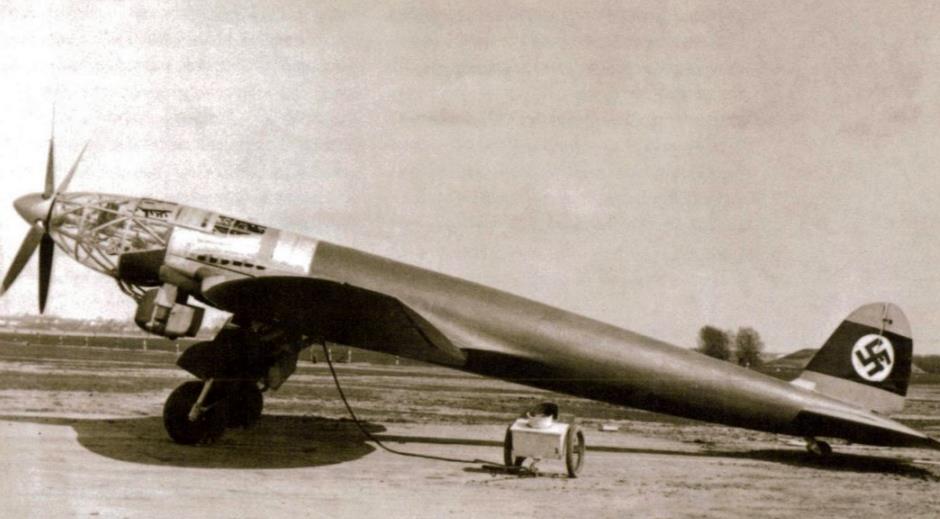




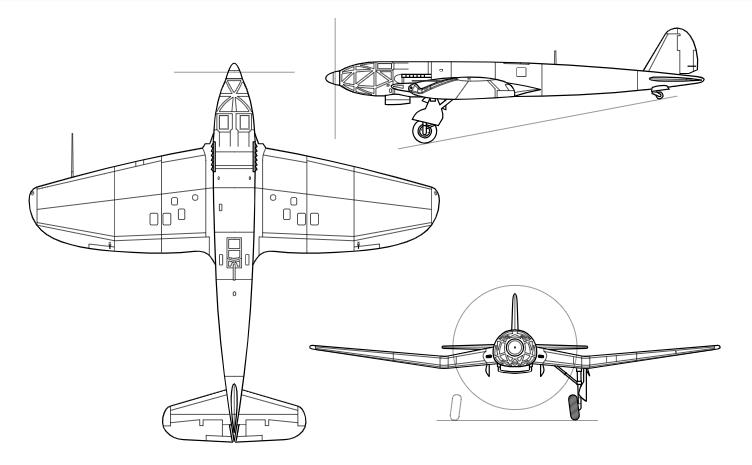
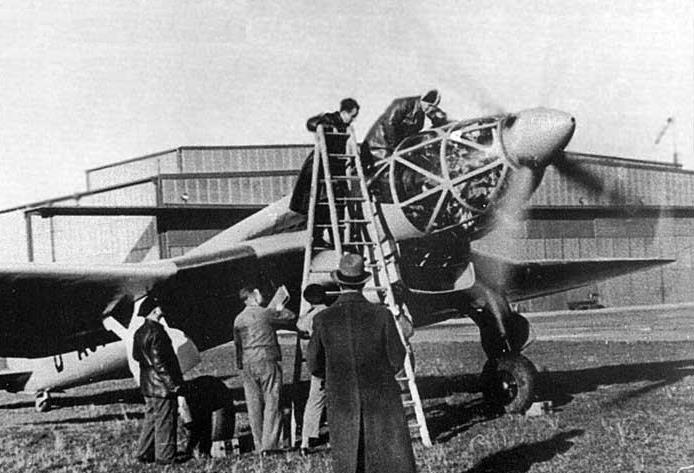
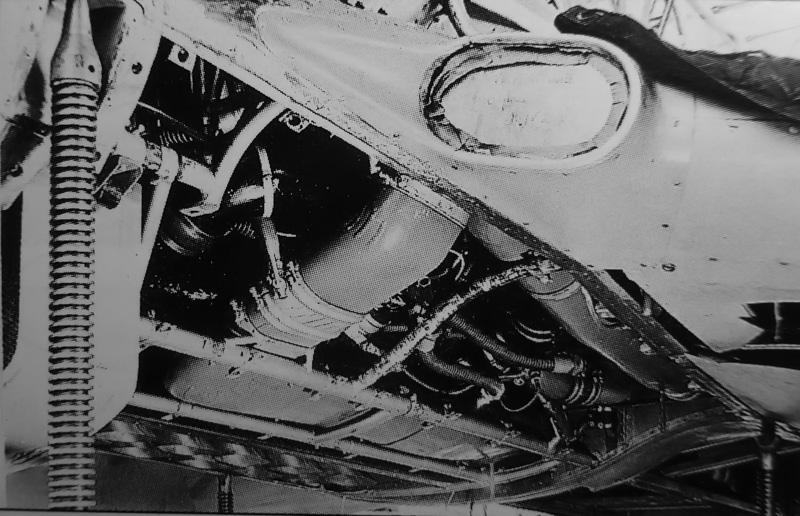
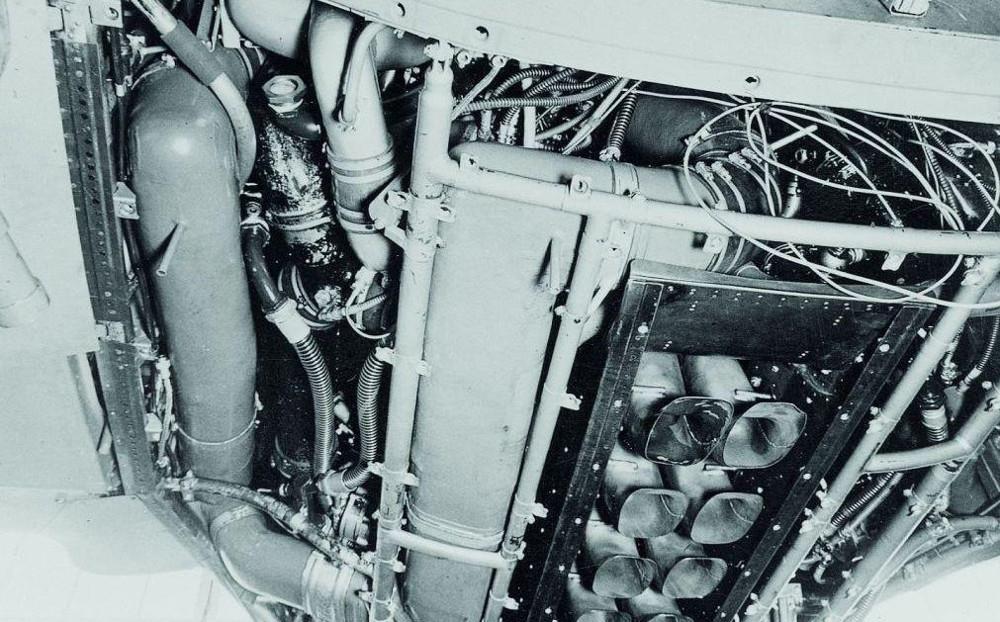
Design was begun in the late summer of 1936. A prominent feature of the aircraft was the streamlined fuselage, which had an extensively glazed cockpit immediately behind the propeller. Two of the three-man crew sat one each side of a driveshaft, which ran aft to a coupled pair of Daimler-Benz DB 601 engines mounted above the wing center-section, mounted together within a common mount (the starboard component engine having a "mirror-image" centrifugal supercharger) with a common gear reduction unit fitted to the front ends of each engine, forming a drive unit known as the DB 606. The He 119 was the first German aircraft to use the "high-power" powerplant system meant to provide German aircraft with an powerplant design of over-1,500 kW (2,000 PS) output capability, but weighing 1.5 tonnes apiece.
The DB 606 was installed just behind the aft cockpit wall, near the center of gravity, with an enclosed extension shaft passing through the centerline of the cockpit to drive a large four-blade variable-pitch propeller in the nose. An evaporative cooling system was used on the V1, with the remaining prototypes having a semi-retractable radiator directly below the engine to augment cooling during take-off and climb.
Only eight prototypes were completed and the aircraft did not see production, mainly because of the shortages of DB 601 "component" engines to construct the 1,500 kg (3,300 lb) DB 606 "power systems" they formed. The first two prototypes were built as land planes, with retractable landing gear. The third prototype (V3) was constructed as a seaplane with twin floats. This was tested at the Erprobungsstelle Travemünde military seaplane test facility on the Baltic coast,
On 22 November 1937, the fourth prototype (V4) made a world class-record flight in which it recorded an airspeed of 505 km/h , with a payload of 1,000 kg , over a distance of 1,000 km The four remaining prototypes were completed during the spring and early summer of 1938, the V5 and V6 being A-series production prototypes for the reconnaissance model, and the V7 and V8 being B-series production prototypes for the bomber model
These four aircraft were three-seaters with a defensive armament of one 7.92 mm MG 15 machine gun in a dorsal position, V7 and V8 having provision for a normal bombload of three 250 kg bombs or maximum bombload of 1,000 kg . V7 and V8 were sold to Japan in May 1940, and extensively studied; the insights thus gained were used in the design of the Yokosuka R2Y.The remaining prototypes served as engine test-beds, flying with various prototype versions of the DB 606 and DB 610 (twinned DB 605s) and the strictly-experimental DB 613 (twinned DB 603).