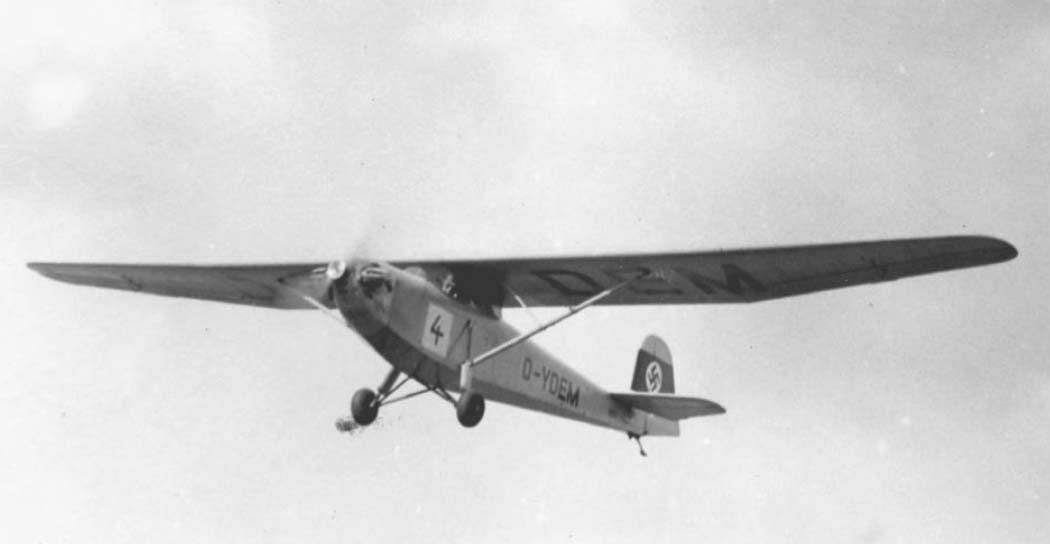
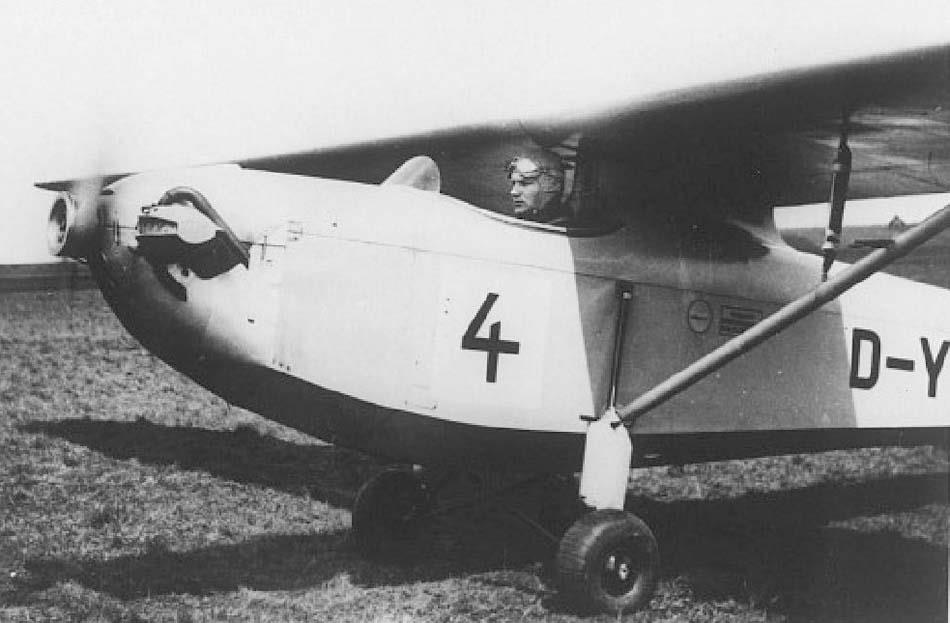
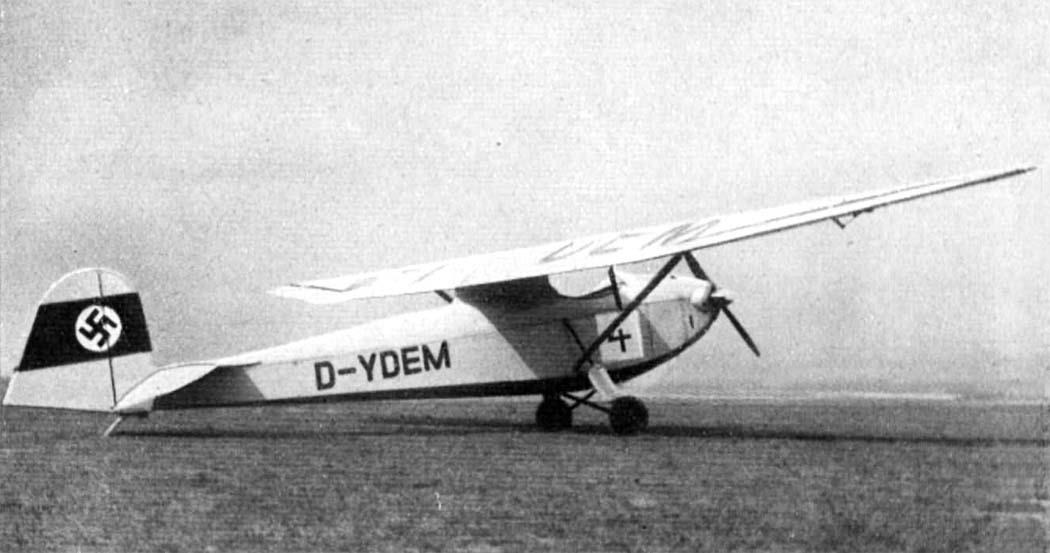



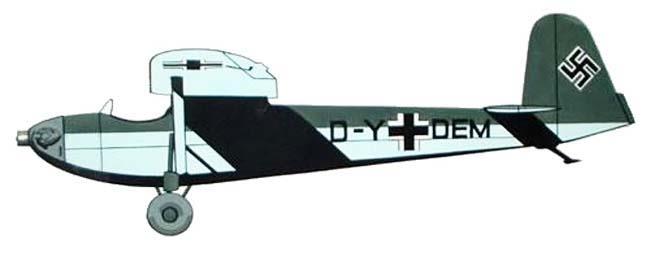



Franz Xaver Mehr , who worked at Erla Maschinenwerk , designed this aircraft as the Me 6 from 1935, mainly on a private initiative in his free time; he hired Johannes Gronert for the static calculations. It was designed in such a way that, with the wings folded, it could be accommodated in a space-saving manner on an area of 1.45 m × 6.60 m and transported on the road by motorcycle. Two people could set it up and take it down. Franz Xaver Mehr was able to convince Erla works manager Wolff von Wedelstaedt to carry out the construction of the motor glider in the Leipzig factory. It was planned to take part in a competition that the NSFK wanted to hold to encourage trainee pilots to switch fromSail - to facilitate on powered aircraft. The flight testing of the aircraft, now known as the Erla 6 A , was carried out at DVL by Heinz Kensche , and at the same time the suitability test of the Schliha engine , which was actually designed for motorcycles, took place . After successful acceptance, the model was assigned the registration D-YDEM . At the motor glider competition held by the NS Fliegerkorps from October 13 to 17, 1937 in Rangsdorf , the Erla 6 A with start number 4 competed against the only other motor glider that took part, the ESM 5 developed by Edmund Schneider. Both aircraft were designed as high- wing monoplanes with nose engines and tail skids. Schneider's design took first place in the elimination round, followed by the Erla 6 A ahead of the other eight aircraft involved. Despite the relatively good performance, the NSFK did not place any order to build more aircraft. The presentation at the aviation fairs in Belgrade in July 1938 and in Brussels in June of the following year, as well as a praising press article from March 1938, did not result in any orders, so that the Erla 6 A remained a one-off.
The Erla 6 A was a braced high - wing monoplane of all-wood construction . The construction was kept simple and the materials used were easy to obtain, so that the aircraft could also be built by aviation groups on their own initiative. The fuselage, formed from wooden frames and chords, was planked with plywood. The front area was designed in such a way that the main landing gear could be replaced by a skid. The engine was attached to an aluminum clad steel mount. The fuel tank was located behind the pilot's seat. The continuous wing consisted of a main and auxiliary spar , a torsion -resistant plywood leading edge, plywood paneling in the front area up to the spar and fabric covering behind. The empennage was cantilevered and made of wood with plywood planked fins and fabric covered rudders. The landing gear consisted of two V-struts and spring struts leading to the upper fuselage chords with two balloon tires 380 × 150 mm and a skid plate at the rear.

| Type |
Single seat motorglider |
| Engine |
1 Schliha air-cooled 2-cyl. boxer engine. Fixed 2-bladed prop.. Fuel capacity 20 l, fuel consumption 7 l/100 km |
| Dimensions |
Length 6.70 m, span 12.30 m, wingarea 15.00 m2 |
| Weights |
Empty 200 kg, flying weight 300 kg |
| Performance |
Max. speed at sea level 125 km/h, cruising speed 110 km/h, landing speed 45 km/h, climb 125 m/min, 9.0 m to 1000 m, range 280 km, service ceiling 3800 m |
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
| 6A |
|
D-YDEM |
Took part in the Light plane contest at Rangsdorf 13 - 17th October 1937. Flown successfully by over 100 pilots before the war, but this prevented further production. |








