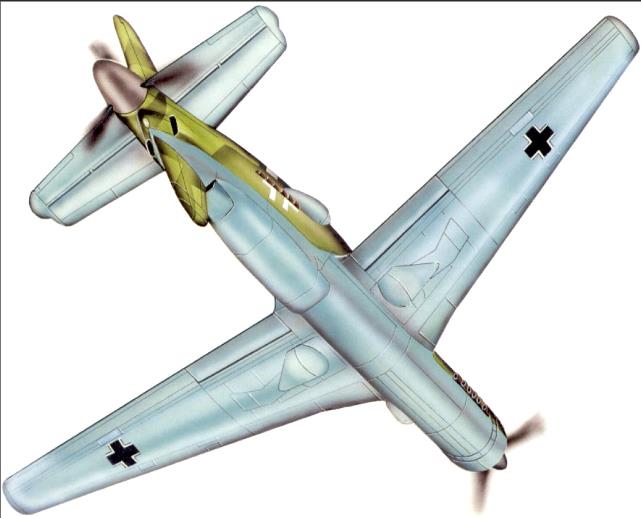
| Type | Single seat fighter with ejection seat and pressure chamber |
| Engine | 2 Daimler-Benz DB 603G with 3,5 m dia. tractor and 3,3 dia. pusher propellers |
| Dimensions | Length 13,70 m, height 5,0 m , span 18,00 m , wing area 45,5 m2 , aspect ratio 7,1 |
| Weights | Empty , loaded 9100 kg , max. take off weight |
| Performance | Max.. speed 835 km/h at 8700 m, 600 km/h at sea level , cruising speed , range , endurance , service ceiling 14000 - 16000 m , climb |
| Armament | 1 30 mm MK 103 in the propeller hub, 2 20 mm MG 151 above the nose engine |