| Type |
1 + 2 seat sportplane |
| Engine |
1 De Havilland Gipsy Major |
| Dimensions |
Length 7,47 m , height 2,67 m , span 11,43 m , wing area 19,1 m2 , |
| Weights |
Empty 586 kg, loaded 1011 kg |
| Performance |
Max.. speed 221 km/h , cruising speed 192 km/h , range 1151 km, service ceiling 6560 m , climb2,8 m/sec. |
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
|
7072 |
D-EGYV, G-ADUL |
Registered Aug. 1934 to Karl Theodor Röchling at Baesweiler, Aachen. In Oct.. 1935 to UK, Airwork Ltd, to Betty Malcolm/Brooklands. Crashed on 23rd Jan. 193 on takeoff at Alicante |
|
7062 |
G-ACSE, A-145, OE-ABC, D-EABC, G-AFZG, AW146 |
Registered in UK 7th July 1934. Sold July 1934 to Osterreichischen Aero Club, to Aero Club von Deutschland. (Nikolaus Eltz) . Sold back to UK Aug.1939 . Impressed. Collided with Oxford N6431 nr Faringdon 30.1.42 |
|
7014 |
G-ACKO, OO-GEJ |
Registered to WH Whitbread /Heston 27/111933. 20/5 1938 to Jacques Lamarche/Brussels. In August 1939 the Belgian Government also requisitioned De Havilland DH.86 Leopard Moth's OO-GEJ which served with the "Estafette Escadrille" and was subsequentely captured by the enemy at Montpellier-Frejorgues in mid-1940 |
|
7094 |
PH-FDK, 963 |
12/3 1935. JEF de Kok at Gravenhage , to NV Nationale Luchvaartschool at Rijswijk. Expired 7/9 1940. Seized by Feldluftpark Holland |
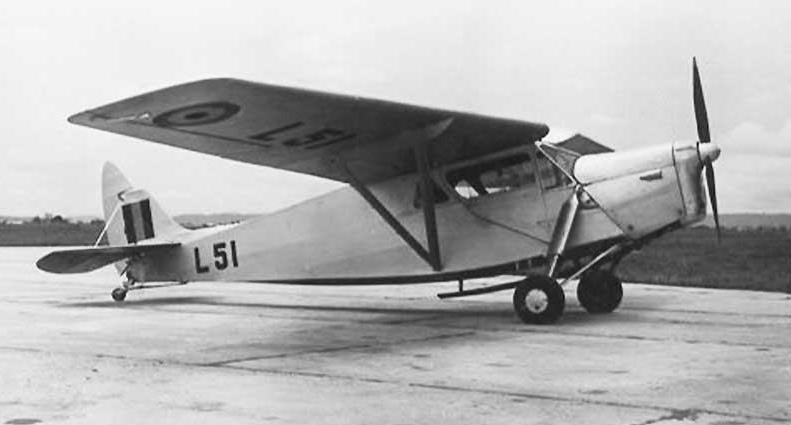
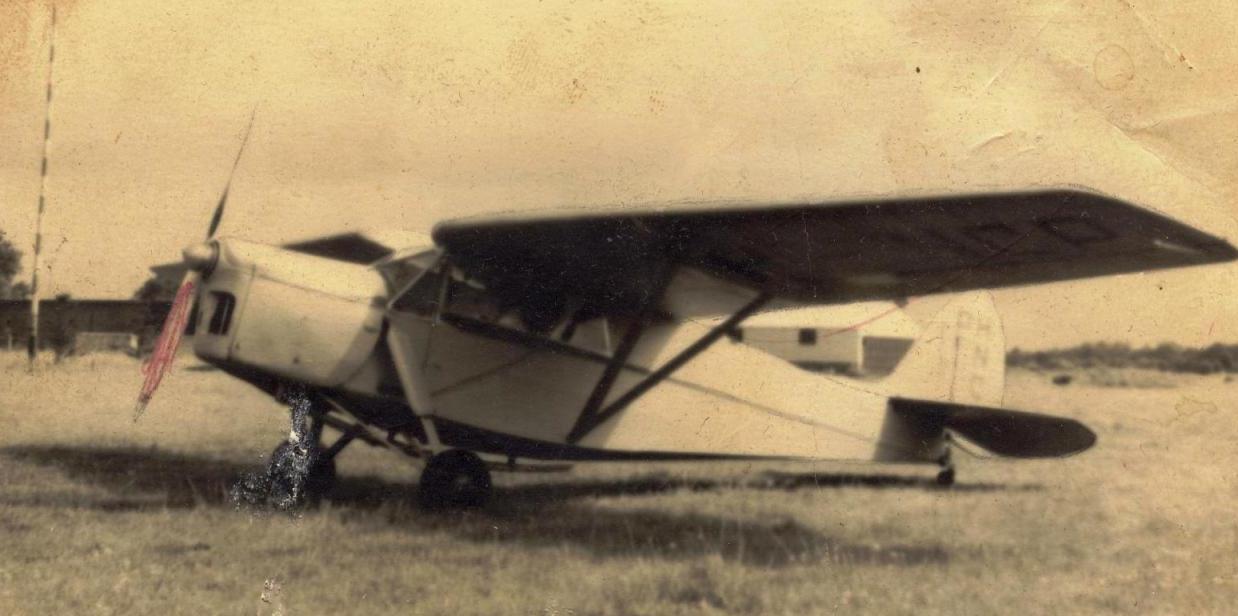
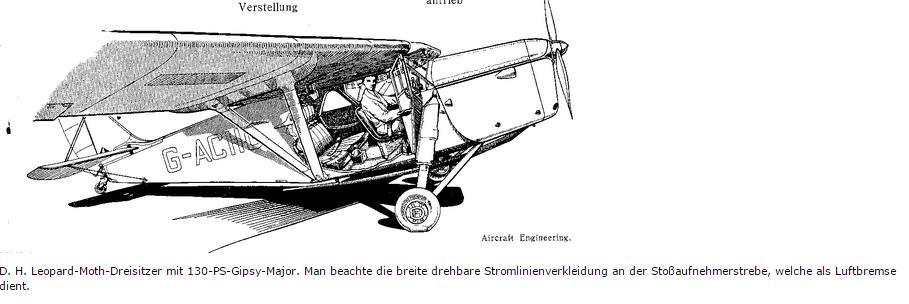
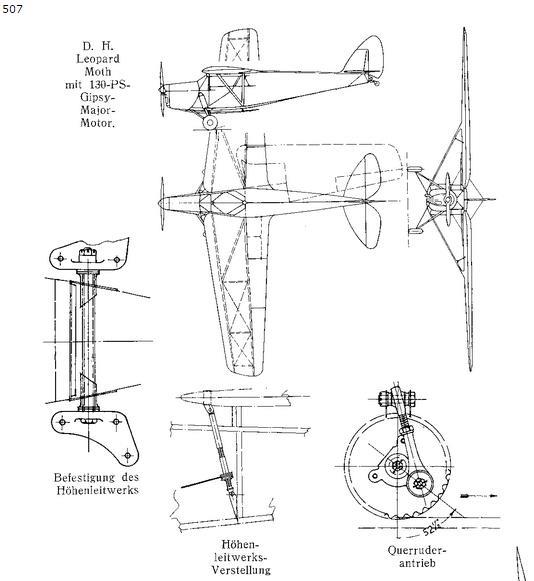
It was a successor to the DH.80 Puss Moth and replaced it on the company's Stag Lane and later Hatfield production lines. It was similar in configuration to the earlier aircraft, but instead of a fuselage with tubular steel framework, a lighter all-plywood structure was used which allowed a substantial improvement in range, performance and capacity on the same type of engine. The pilot is seated centrally in front of two side-by-side passengers and the wings can be folded for hangarage.
The prototype first flew on 27 May 1933 and in July won the King's Cup Race at an average speed of 224.5 km/h, piloted by Geoffrey de Havilland. A total of 133 aircraft were built, including 71 for owners in the British Isles, and 10 for Australia. Other examples were exported to France, Germany, India, South Africa and Switzerland. Production of the Leopard Moth ended in 1936.
44 Leopard Moths were impressed into military service in Britain and others in Australia during World War II, mostly as communications aircraft. Only a few managed to survive six years of hard usage although a small number were still airworthy seventy years after the last was completed. Six remained operational in the U.K. in 2009.