| Type |
2-seat sportplane |
| Engine |
1 Pobjoy Cataract II |
| Dimensions |
Length 8 m , height 2,15 m, span 13 m , wing area 20 m2 , |
| Weights |
Empty 435 kg, loaded , max. take off weight 680 kg |
| Performance |
Max.. speed 167 km/h, cruising speed 145 km/h , range 676 km, endurance , service ceiling 5180 m , climb |
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
| Klemm L25 c -1A |
|
D-ECOQ |
|
| Klemm L25 c XI |
6 |
G-ACOE D-ECOE |
Walter Bassenge/ Oberwiesenfeld 1936 |
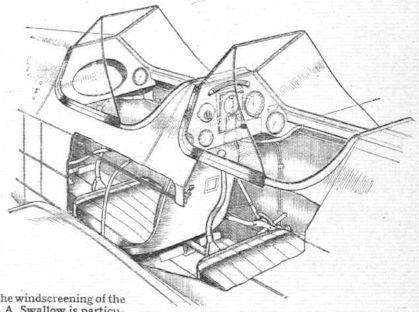
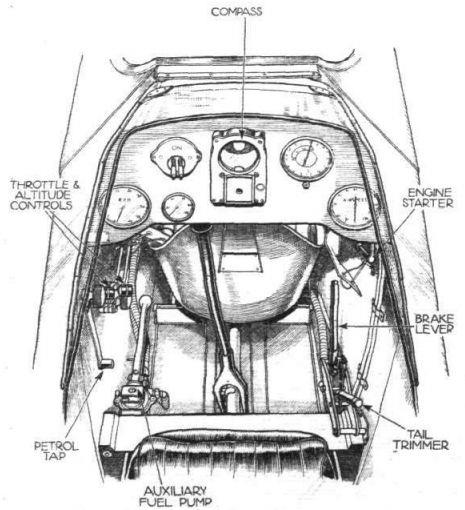
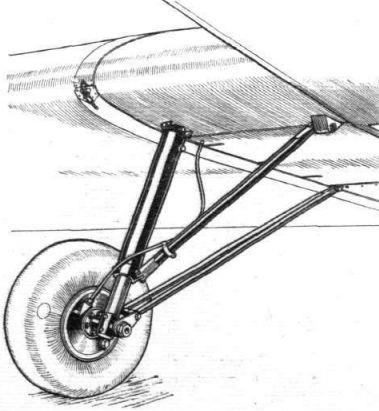
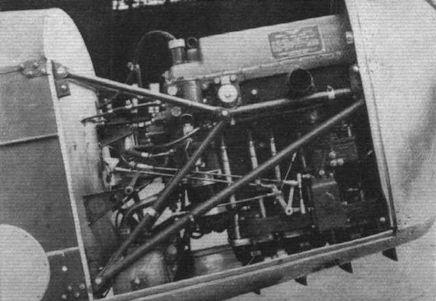
A German two-seat light aircraft distinguished by its reliability and excellent low-thrust performance, the Klemm L.25 first flew in 1927. In 1933 The British Klemm Aeroplane Company was founded to build this aircraft in the UK. The British prototype first flew in November 1933. and was distinguished by the fact that some parts of the structure were strengthened in accordance with British airworthiness standards. It was a cantilever low- wing aircraft of wooden construction with fabric-covered control surfaces, and had folding wings, two tandem open cockpits, a fixed landing gear with a tail spike and a reliable low-thrust engine.
The initial production version was designated British Clemm L.25C 1A Swallow. The prototype and five other aircraft were powered by a British Salmson AD9 piston engine producing 63 kW (85 hp); all the others, with the exception of one. had a Pobjoy Cataract II radial engine with 63 kW (85 hp). After the first 28 aircraft were built, the wing, stabilizer, fin and rudder took on angular shapes. At this time the company changed its name to Aircraft Manufacturing Company, resulting in the Swallow being renamed British Aircraft Swallow 2. More than 100 aircraft were built with the 67 kW (90 hp) Pobjoy Cataract III or Blackburn Cirrus Minor 1 engines with the same performance.



