| Type | 3-seat bomber | 2-seat bomber | 3-seat bomber |
| Ar E.555-1 | Ar E.555-3 | Ar E.555-6 | |
| Engine | 6 BMW 003 | 2 BMW 018 | 3 BMW 018 |
| Dimensions | Length , height 5,0 m, span 21,2 m, wing area 125 m2 , | Length 18,4 m , height , span 21,2 m , wing area 125 m2 , | Length 12,35 m m , height 3,74 m , span 28,4 m , wing area 160 m2 , |
| Weights | Empty , loaded 24000 kg , max. take off weight | Empty , loaded 25200 kg , max. take off weight , fuel 10000 kg | Empty , loaded 25200 kg , max. take off weight , fuel 18750 kg |
| Performance | Max.. speed 860 km/h , cruising speed , range 4800 km , endurance , service ceiling 15000 m , climb | Max.. speed 915 km/h , cruising speed , range 4000 km, endurance , service ceiling , climb | Max.. speed 920 km/h , cruising speed , range 7500 km, endurance , service ceiling , climb |
| Armament | Bombload 4000 kg | Bombload 4000 kg | Bombload 4000 kg |
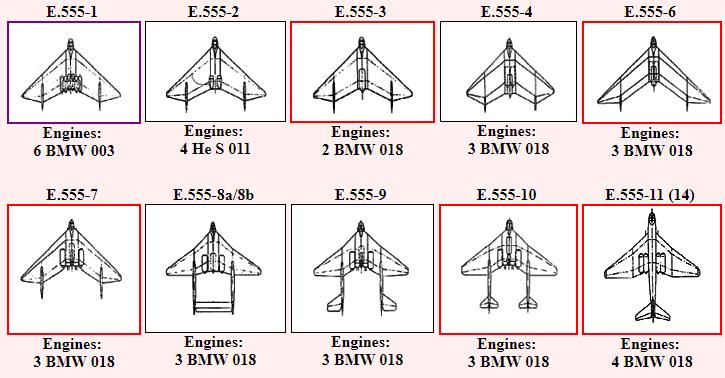
In mid-December 1943, at the Arado facilities in Landeshut/Schlesien, work began on a flying wing project series under the direction of Dr.-Ing. W. Laute. This was further elaborated by Dipl. Ing. Kosin and Lehmann of Arado under the title of "Long Range/High Speed Flying Wing Aircraft". A discussion took place with the RLM several months later in early 1944, and Arado was asked to compile design studies for a long range jet powered bomber. Since the requirements were high speed, a bomb load of at least 4000 kg (8818 lbs) and a range of 5000 km (3107 miles), it was realized that the project could best be fulfilled by using a flying wing design with a laminar high speed profile. The number of designs eventually reached fifteen, and included strategic bombers, remote controlled weapons carriers and fighters.
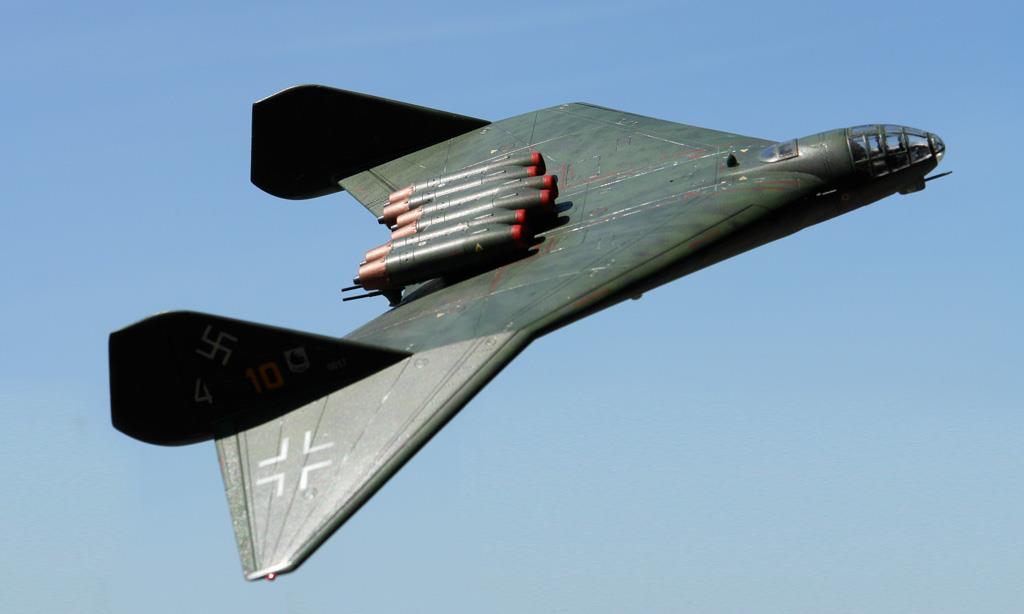
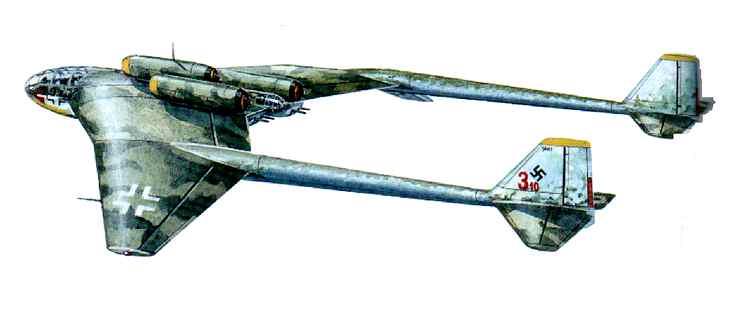
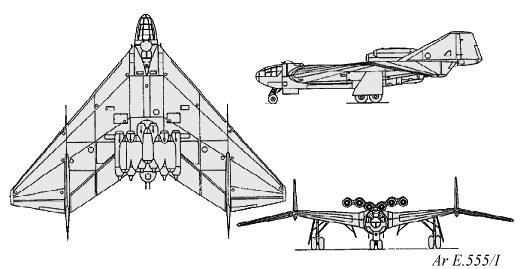
The Arado Ar E.555-1 was constructed entirely of metal (both steel and Duraluminum), and was basically a flying wing with a short, circular cross section forward fuselage where the pressurized cockpit was located. There were two large vertical fins and rudders that sat 6.2 m (20' 4") from the centerline of the aircraft. The main landing gear undercarriage consisted of two tandem, dual wheeled units that retracted inwards into the wing, and the front landing gear was a single, dual wheeled unit that retracted to the rear to lie beneath the cockpit. A droppable auxialiary landing gear could be used for overload conditions. Power was to be provided by six BMW 003A, all located on the rear upper surface of the wing. Defensive armament consisted of two MK 103 30mm cannon in the wing roots near the cockpit, a remote controlled turret armed with two MG 151/20 20mm cannon located just behind the cockpit and a further two MG 151/20 20mm cannon in a remote controlled tail turret, which was controlled via a periscope in a pressurized weapons station behind the cockpit area.
On December 28, 1944, Arado was ordered to cease all work on the E.555 series, probably due to the worsening war situation, and the need to concentrate aircraft development and production on fighters.
The Arado Ar E.555-1 was constructed entirely of metal (both steel and Duraluminum), and was basically a flying wing with a short, circular cross section forward fuselage where the pressurized cockpit was located. There were two large vertical fins and rudders that sat 6.2 m (20' 4") from the centerline of the aircraft. The main landing gear undercarriage consisted of two tandem, dual wheeled units that retracted inwards into the wing, and the front landing gear was a single, dual wheeled unit that retracted to the rear to lie beneath the cockpit. A droppable auxialiary landing gear could be used for overload conditions. Power was to be provided by six BMW 003A, all located on the rear upper surface of the wing. Defensive armament consisted of two MK 103 30mm cannon in the wing roots near the cockpit, a remote controlled turret armed with two MG 151/20 20mm cannon located just behind the cockpit and a further two MG 151/20 20mm cannon in a remote controlled tail turret, which was controlled via a periscope in a pressurized weapons station behind the cockpit area.
On December 28, 1944, Arado was ordered to cease all work on the E.555 series, probably due to the worsening war situation, and the need to concentrate aircraft development and production on fighters.
| Type | 3-seat bomber | 3-seat bomber | 2-seat bomber |
| Ar E.555-7 | Ar E.555-10 | Ar E.555-11 | |
| Engine | 3 BMW 018 | 3 BMW 018 | 4 BMW 018 |
| Dimensions | Length 8,8 m , height 3,65 m, span 25,2 m , wing area 160 m2 , | Length 19,2 m , height , span 23,66 m , wing area 140 m2, | Length 25,1 m , height 4,1 m , span 23,66 m, wing area 140 m2 , |
| Weights | Empty , loaded 41300 kg, max. take off weight , fuel 15700 kg | Empty , loaded 47845 kg , max. take off weight | Empty , loaded 47000 kg , max. take off weight |
| Performance | Max.. speed 950 km/h, cruising speed , range 5000 km, endurance , service ceiling , climb | Max.. speed 920 km/h , cruising speed , range 6400 km, endurance , service ceiling , climb | Max.. speed 1020 km/h, cruising speed , range 8000 km, endurance , service ceiling , climb |
| Armament | Bombload 4000 kg | Bombload 4000 kg | Bombload 6000 kg |
The Arado E.555 was a long range strategic bomber proposed by the German Arado company during World War II in response to the RLM's Amerikabomber project. The E.555 designation was applied to a series of long range jet bomber designs of various sizes, powerplant, crew and weapon load configurations. As design studies only, no aircraft were developed or constructed and the entire E.555 project was cancelled at the end of 1944.
In 1942, the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (Reich Air Ministry, RLM) put forward an initiative to obtain a long-range bomber for the Luftwaffe that would be capable of striking the continental United States from Germany. Requests for designs were made to the major German aircraft manufacturers early in World War II, long before the U.S. had entered the war. Arado had begun its own independent project design work for a future jet flying wing bomber in late 1943; up until that time other manufacturers, such as Heinkel (by the February 1943 timeframe), Messerschmitt, Focke-Wulf and Junkers had piston-engined intercontinental bomber designs under various stages of consideration and initial prototype testing per the RLM's request. Arado had also developed its own small, shorter-range jet bomber, the Ar 234 Blitz, which first flew in June 1943. By early 1944, Arado was asked to compile design studies for a long-range jet-powered bomber.
Several different E.555 design configurations were proposed and considered; the Arado team's overall goal for the project was an aircraft with high speed, long range and capable of carrying a four-ton (4,000 kg) bomb load. Perhaps the most striking was the E.555 I, a six-jet, angular flying wing design with remotely-operated defensive turrets. The trijet E.555 VI had the longest wingspan of all the proposals at 28.4 m (93 ft) and range (carrying supplementary fuel tanks) of 7,500 km The aircraft were to be powered using a jet engine which had not completed development as of 1944, the 34.3 kN thrust BMW 018; from two to six of these powerplants in each of the proposed E.555 designs.
All of the E.555 projects were abandoned, following a 22 December 1944 order by the Reich Air Ministry.
Arado E.555 I
Six-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 II
Four-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 III
Twin-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 IV
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 VI
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 VII
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 VIII
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 IX
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 X
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 XI
Four-engine bomber[
In 1942, the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (Reich Air Ministry, RLM) put forward an initiative to obtain a long-range bomber for the Luftwaffe that would be capable of striking the continental United States from Germany. Requests for designs were made to the major German aircraft manufacturers early in World War II, long before the U.S. had entered the war. Arado had begun its own independent project design work for a future jet flying wing bomber in late 1943; up until that time other manufacturers, such as Heinkel (by the February 1943 timeframe), Messerschmitt, Focke-Wulf and Junkers had piston-engined intercontinental bomber designs under various stages of consideration and initial prototype testing per the RLM's request. Arado had also developed its own small, shorter-range jet bomber, the Ar 234 Blitz, which first flew in June 1943. By early 1944, Arado was asked to compile design studies for a long-range jet-powered bomber.
Several different E.555 design configurations were proposed and considered; the Arado team's overall goal for the project was an aircraft with high speed, long range and capable of carrying a four-ton (4,000 kg) bomb load. Perhaps the most striking was the E.555 I, a six-jet, angular flying wing design with remotely-operated defensive turrets. The trijet E.555 VI had the longest wingspan of all the proposals at 28.4 m (93 ft) and range (carrying supplementary fuel tanks) of 7,500 km The aircraft were to be powered using a jet engine which had not completed development as of 1944, the 34.3 kN thrust BMW 018; from two to six of these powerplants in each of the proposed E.555 designs.
All of the E.555 projects were abandoned, following a 22 December 1944 order by the Reich Air Ministry.
Arado E.555 I
Six-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 II
Four-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 III
Twin-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 IV
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 VI
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 VII
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 VIII
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 IX
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 X
Three-engine flying wing bomber
Arado E.555 XI
Four-engine bomber[