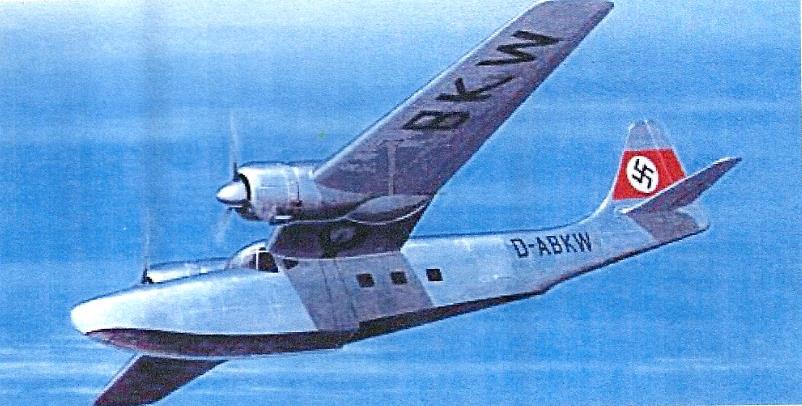
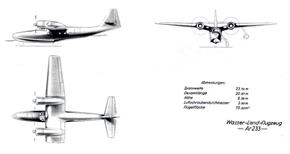
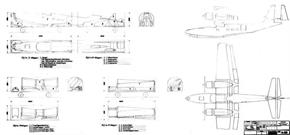
| Type | 2 (3) + 10 (8) airliner |
| Engine | 2 Bramo 323 MA with 2 electrically started 3-bladed propeller, dia. 3,50 m |
| Dimensions | Length 20,87 m, height 6,55 m , span 23,70 m, wing area 75,0 m2 , wheel width nose wheel 875 x 325 mm - main wheel 1015 x 380 mm |
| Weights | Empty , loaded 9000 kg, max. take off weight |
| Performance | Max.. speed 304 km/h , cruising speed , range 1200 km, endurance , service ceiling , climb |
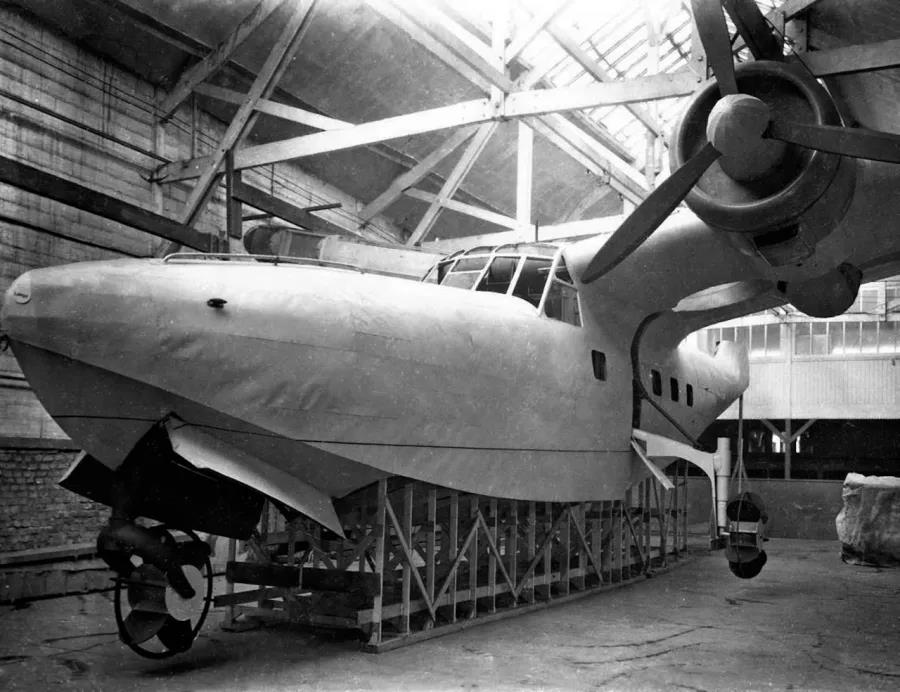

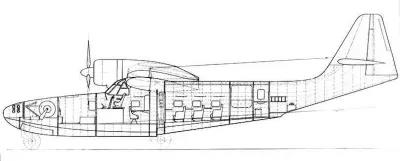



The Ar 233 was a twin-engined flying-boat with room for ten passengers. It would have been powered by either two BMW 323 or BMW 801 engines.[1] A retractable tricycle landing gear would have allowed amphibious operation.[1] A mockup was completed by Dewoitine in German-occupied France, but the project was abandoned due to the Liberation of France in 1944.
The Arado Ar 233 was intended for civilian use only but, later on in the development process, the Germans wanted to weaponize it and make it suitable for combat. Some aircraft firms that worked for the axis power, were thinking about post war German civil aircraft early in the 1940s, in accordance with a request made by the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM/German aviation ministry). Some examples of aircraft designed for Germany for future civilian use are the Fw 206 and the BV 144. The Arado firm responded with their own two engine float plane design because of the Fw 206 and BV 144. The Ar 233 project began around August and bore the company designation E 430 and initially the RLM designation Ar 430. Two variants were envisaged, one being a Bramo 323 R2 powered seaplane model capable of transporting ten passengers, and the other powered by the Argus Ar 204, which was scrapped for in favor of the much more superior Bramo 323 R2.
The Arado Ar 233 was intended for civilian use only but, later on in the development process, the Germans wanted to weaponize it and make it suitable for combat. Some aircraft firms that worked for the axis power, were thinking about post war German civil aircraft early in the 1940s, in accordance with a request made by the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM/German aviation ministry). Some examples of aircraft designed for Germany for future civilian use are the Fw 206 and the BV 144. The Arado firm responded with their own two engine float plane design because of the Fw 206 and BV 144. The Ar 233 project began around August and bore the company designation E 430 and initially the RLM designation Ar 430. Two variants were envisaged, one being a Bramo 323 R2 powered seaplane model capable of transporting ten passengers, and the other powered by the Argus Ar 204, which was scrapped for in favor of the much more superior Bramo 323 R2.