| Type |
RK 9 Two seat sportplane |
RK 9a Two seat sportplane |
RK 9b Two seat seaplane |
| Engine |
1 Anzani 35 hp |
1 Salmson AD 9 |
|
| Dimensions |
Length 6,85 m, height 2,30 m , span 8,96 m, wing area 19,64 m2, aspect ratio 4 |
Length 6,60 m, height 2,30 m , span 8,96 m, wing area 19,64 m2, aspect ratio 4 |
|
| Weights |
Empty 250 kg, flying weight 450 kg, fuel 30 kg, oil 5 kg, pilot 80 kg, payload 85 kg, wing loading 22,90 kg/m2 |
Empty 275 kg, flying weight 475 kg, fuel 30 kg, oil 5 kg, pilot 80 kg, payload 85 kg, wing loading 24,2 kg/m2 |
|
| Performance |
Max. speed 120 km/h, cruising speed 100 km/h, climb 1,3 m/sec., service ceiling 3000 m, range 400 km, startlength 50 m, landing speed 45 km/h |
Max. speed 120 km/h, cruising speed 100 km/h, climb 1,5 m/sec., service ceiling 3500 m, range 400 km, startlength 40 m, landing speed 45 km/h |
|
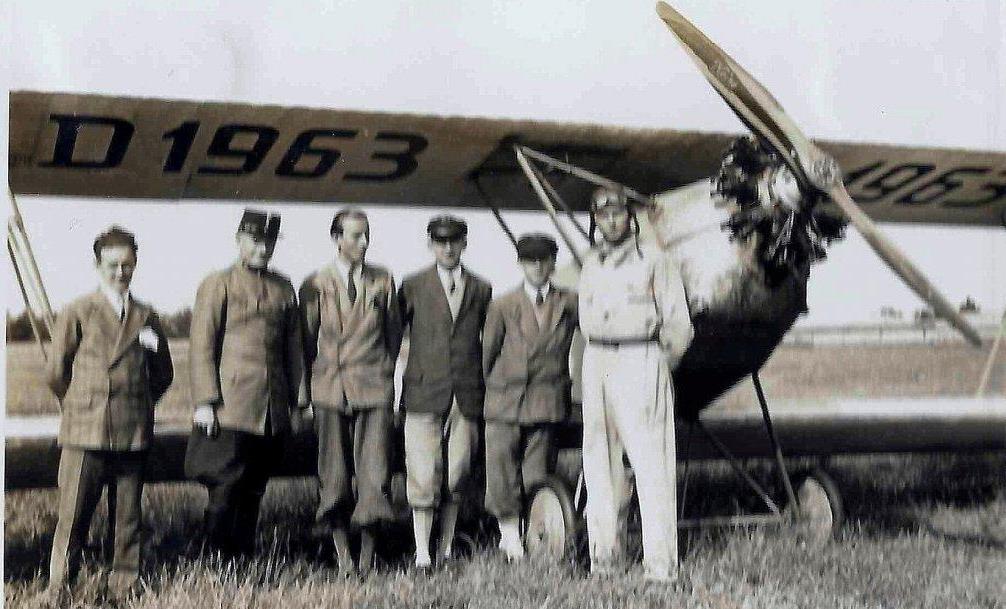
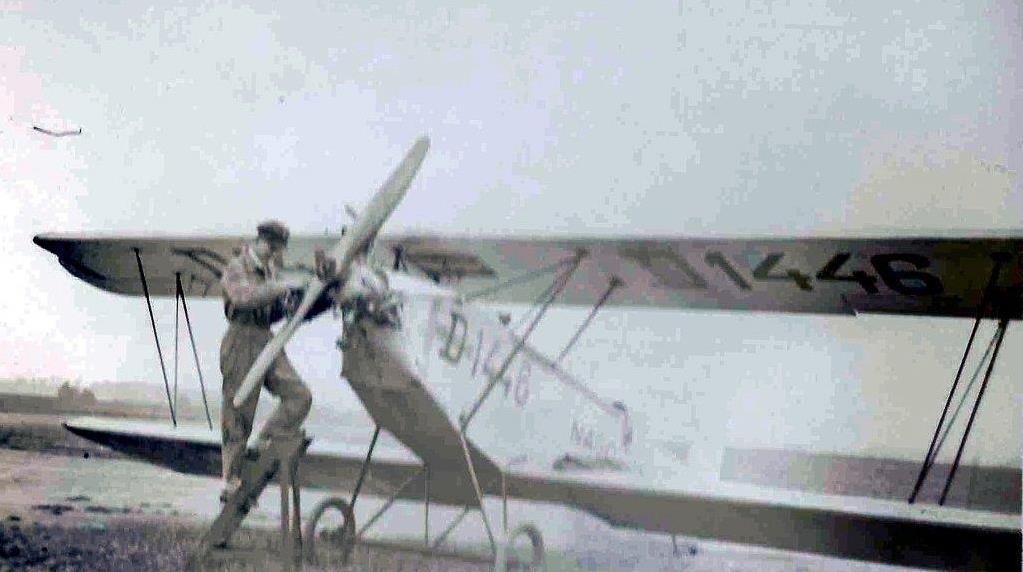
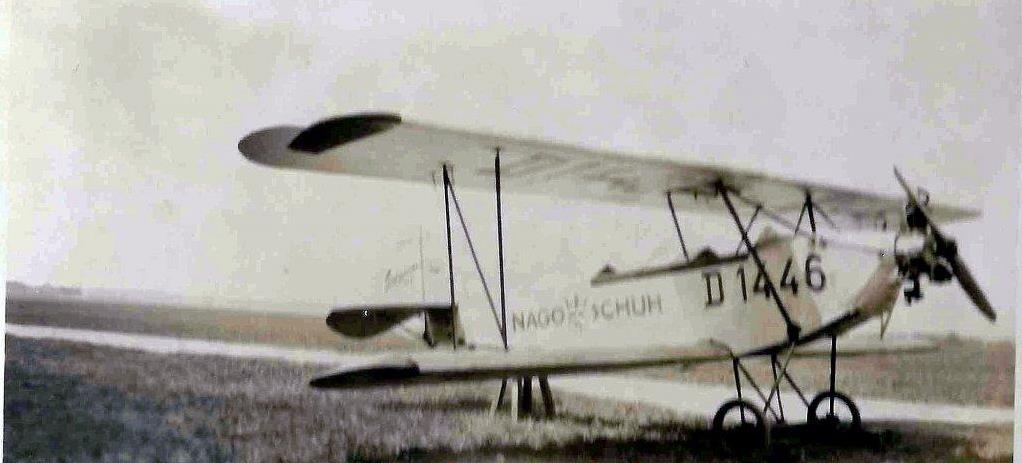
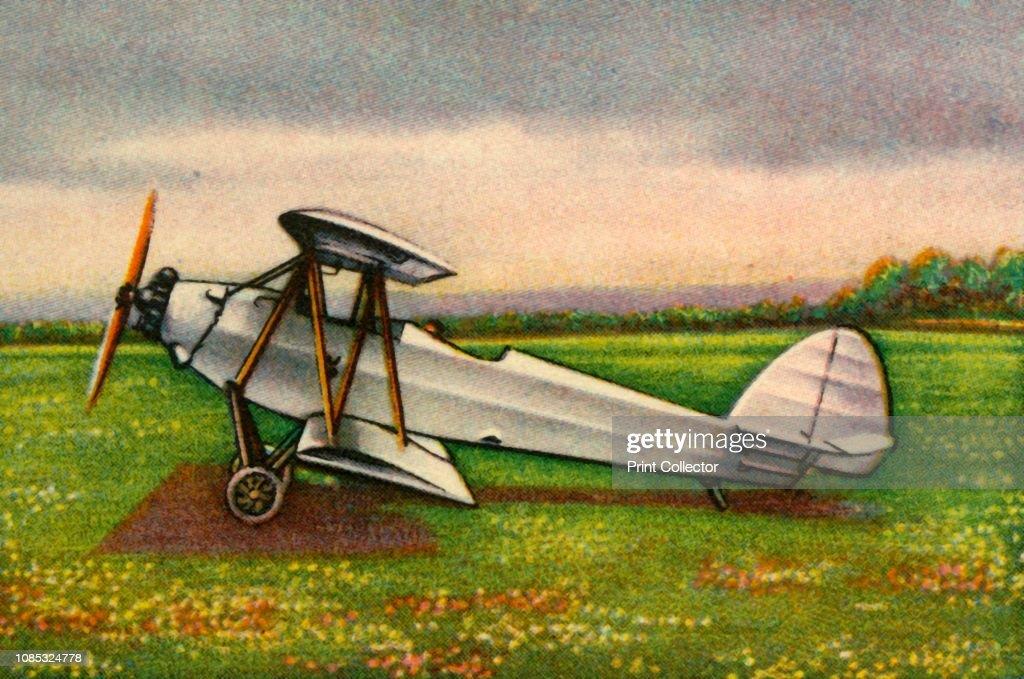
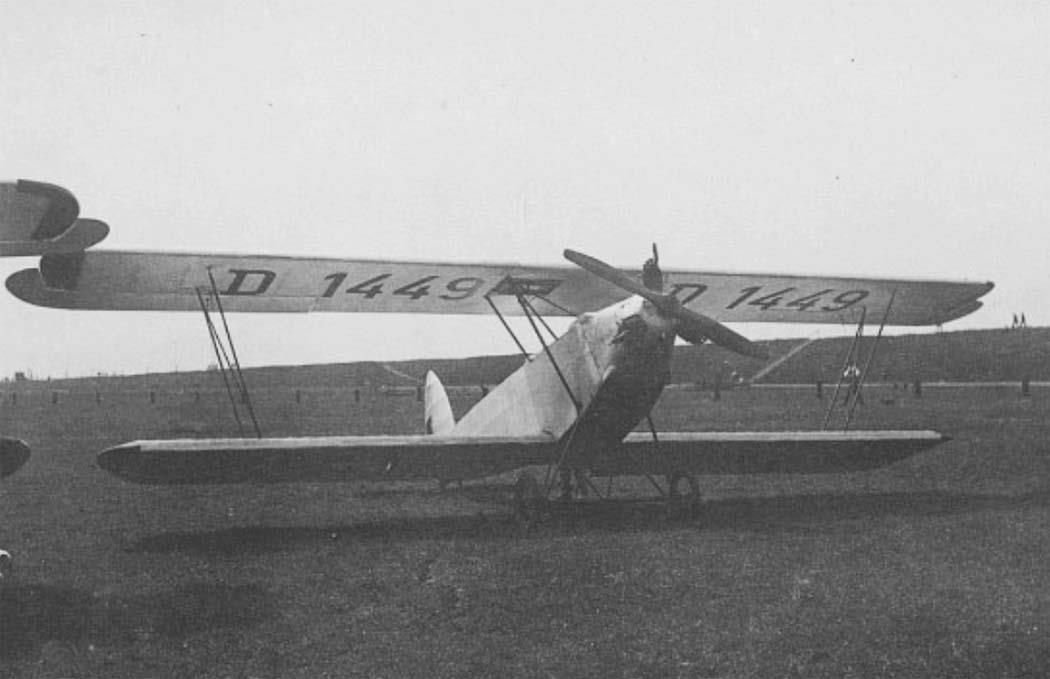
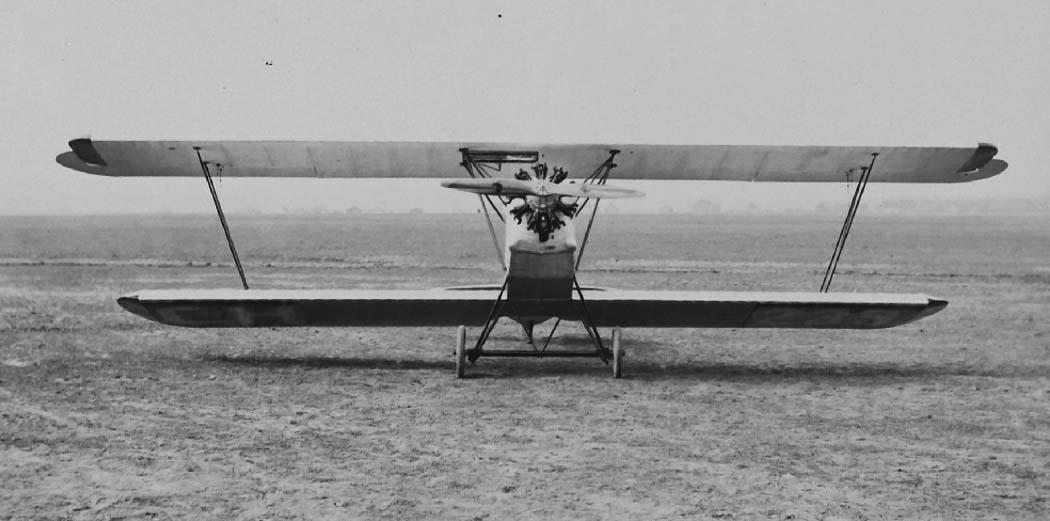
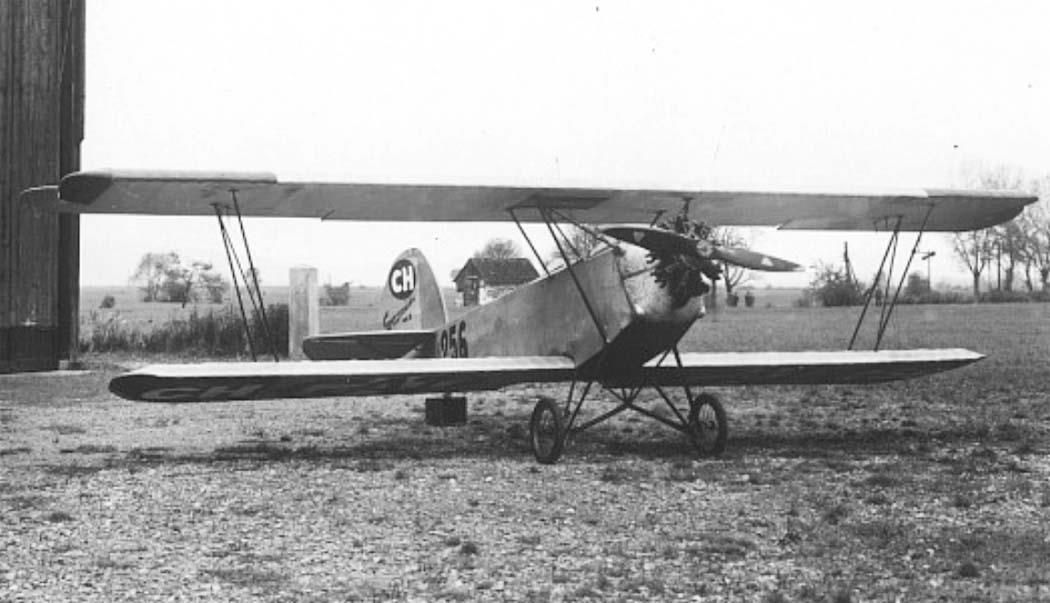
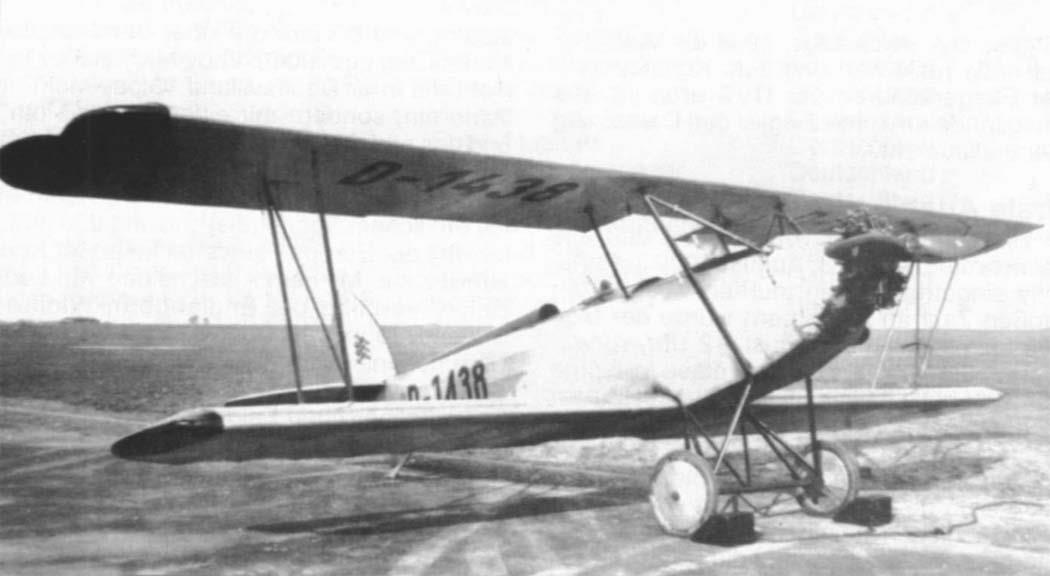
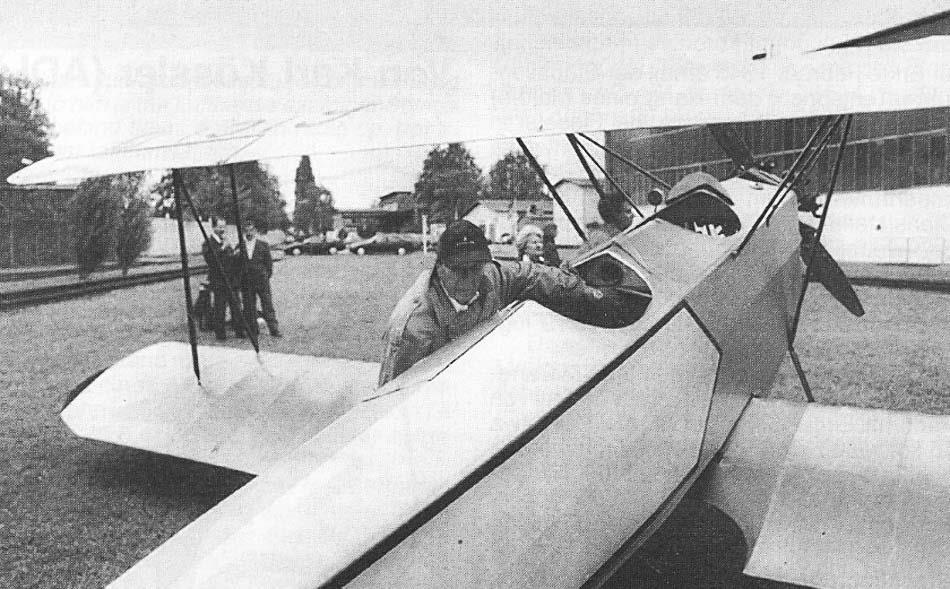
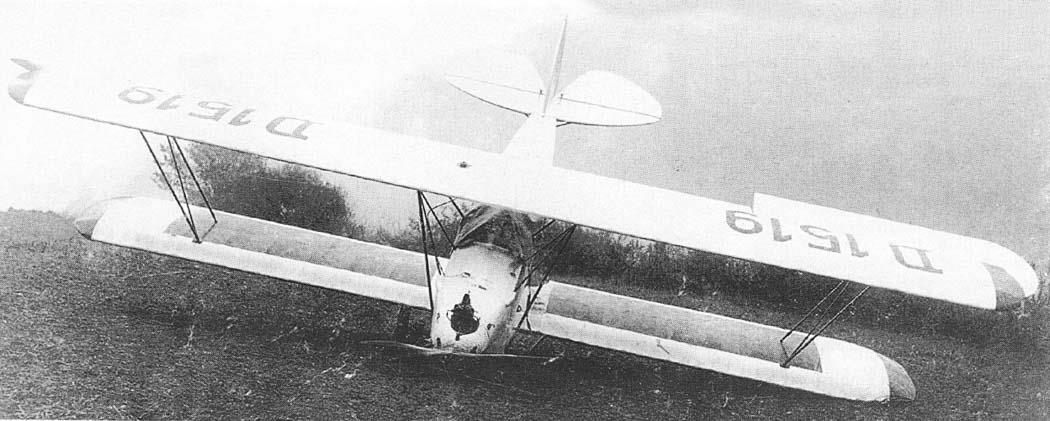
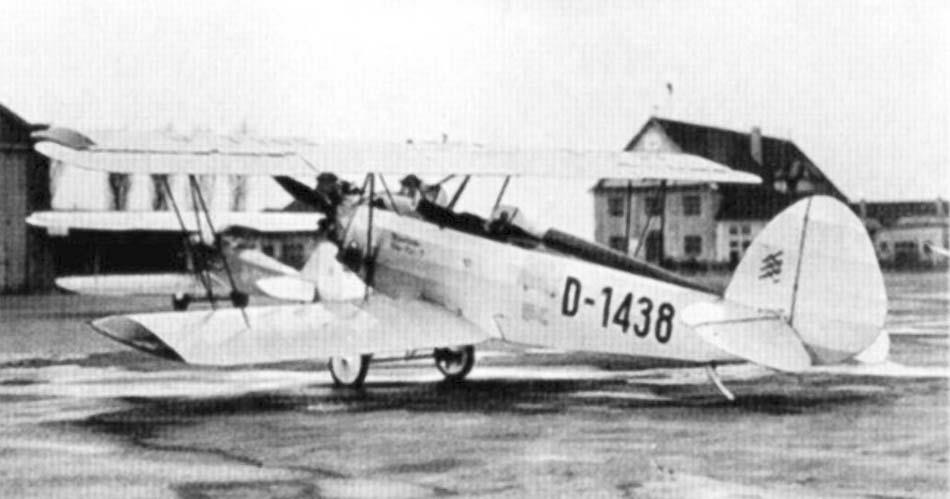











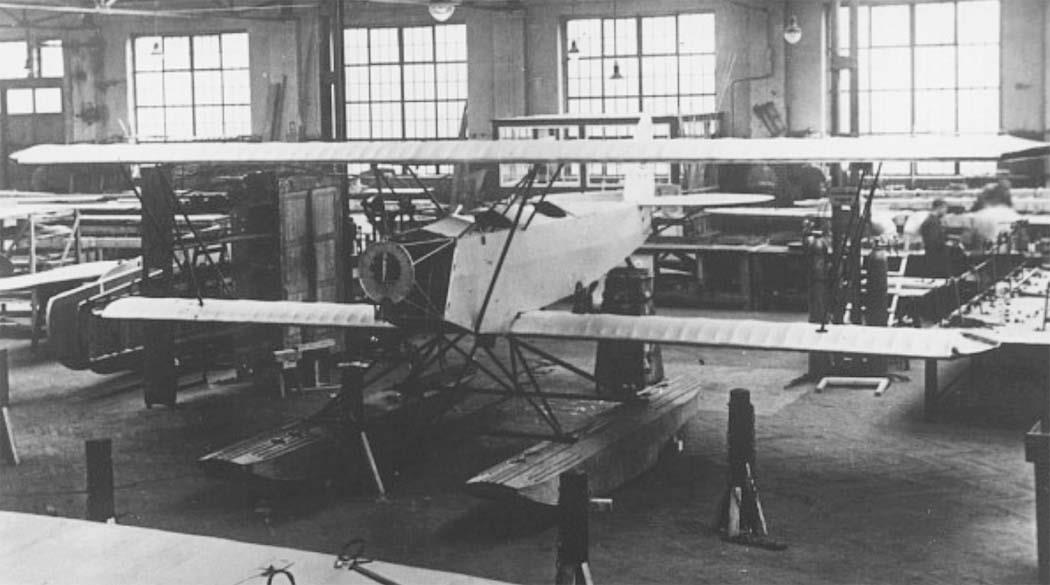

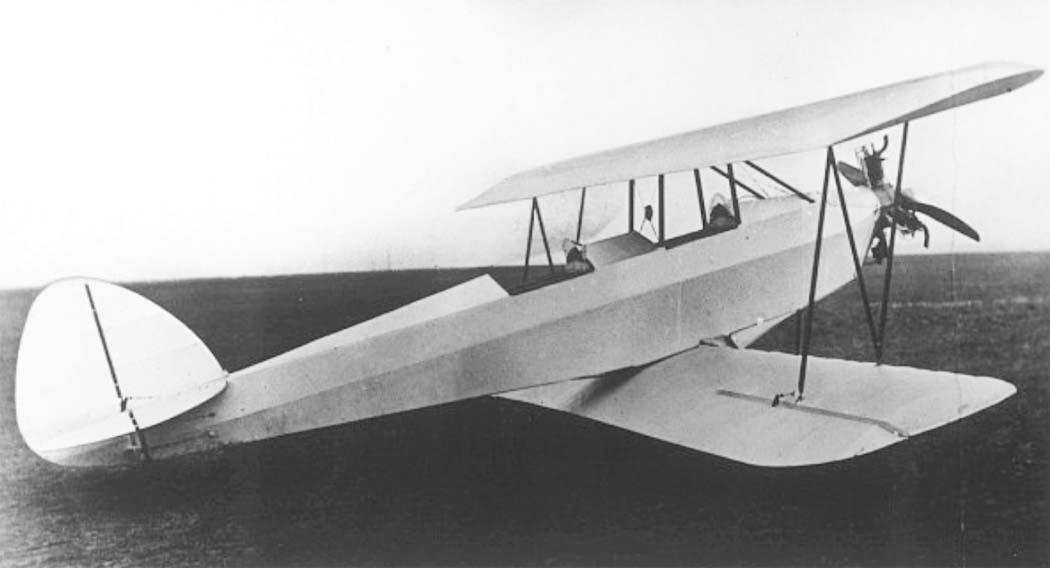






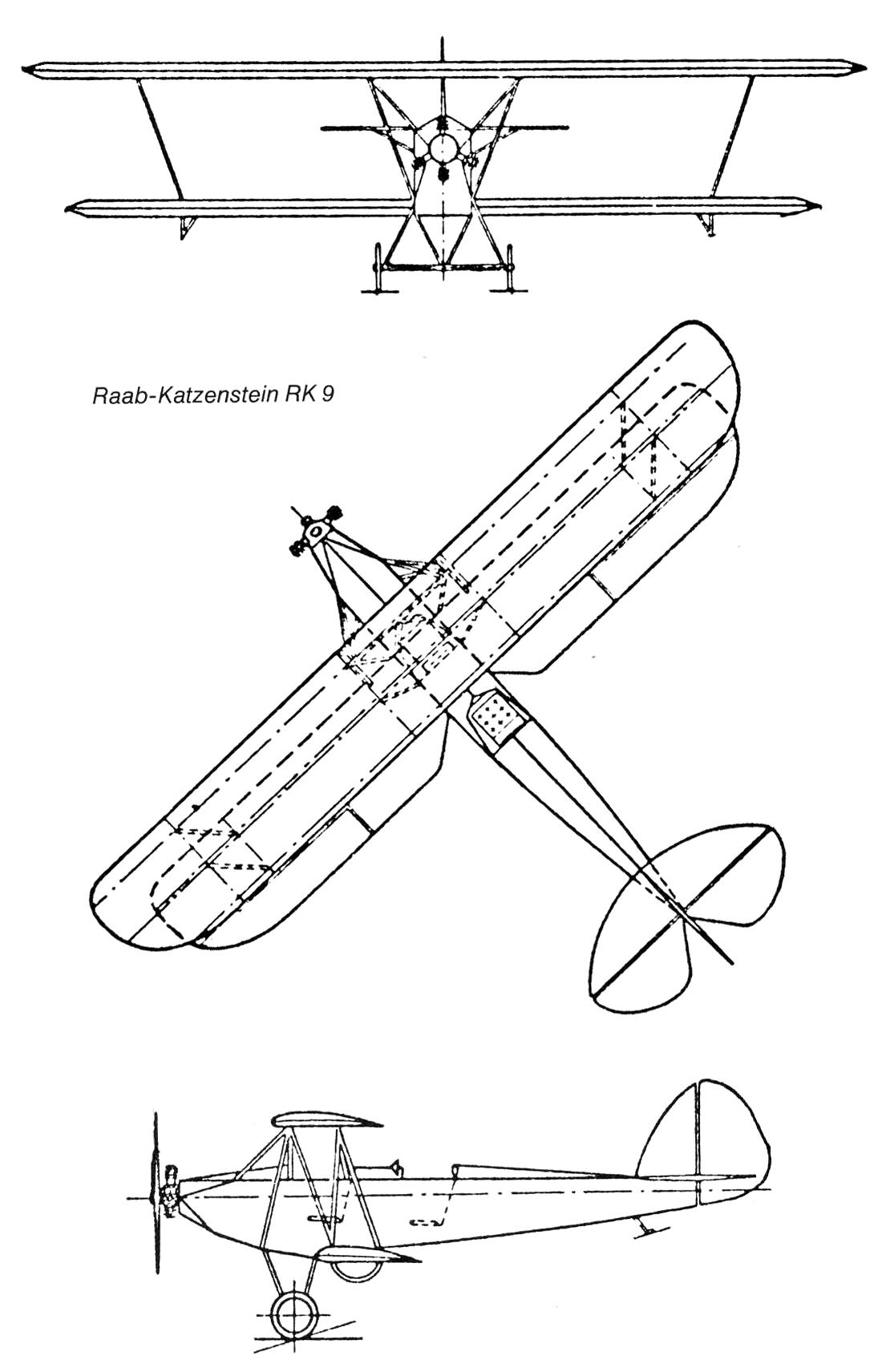
RK. 9 "Grasmücke", the new German light aircraft.
After several months of design and production work, the Raab-Katzenstein aircraft works have released a light aircraft (see "Der Flug", 10th year, No. 5, page 83) that is built as a biplane. The aircraft costs the currently unmatched low price for a biplane of just 6900 RM, complete with airworthiness certificate, ex works Kassel. With their extremely healthy pricing policy in the aircraft industry, the works are accelerating a development that required decades of work, experience and concentration in the leading automobile industry, which is friendly to the works. The first series of 20 units is even to be sold at the introductory price of just 5900 RM per aircraft.
The technical details are as follows:
Central fuselage between wings, seats one behind the other, dual controls. Biplane, staggered, cantilevered with torsion bars. Engine mounted in the nose of the fuselage on a steel tube foundation with shock absorbers in between, working on a traction propeller. Tail unit and rudder with normal elliptical outline, horizontal stabilizer braced once against the fuselage, rudder unbalanced, ailerons on the upper wing.
Material and design of the fuselage: steel tube frame with tube diagonals in the edges and wire crossovers in the horizontal planes, fabric covering.
Material and design of the wings: normal wooden construction, I-spars, lattice spars, inner posts and wing tips, dural tube, inner bracing, steel wire. Aspect ratio of the wing: 1:7.5 at the top, 1:6.7 at the bottom. Angle of the wings at the top: 0.5°, at the bottom 1.0°. V-position of the wings 0°.
Material and design of the tail unit:
wooden frame, fabric covered. Landing gear and skid: Normal steel tube, landing gear, rubber cord suspension, skid made of duralumin tube.
Crew: One pilot and one passenger or student pilot.
Powerplant: Engine: three-cylinder Anzani, air-cooled; Engine power about 35 hp; Propeller drive: direct; Fuel transport: natural gradient;
Fuel storage: Tank in the upper wing; Fuel capacity: 42 liters.R.K. 9 "Grasmücke", the new German light aircraft.
After several months of design and production work, the Raab-Katzenstein aircraft works have released a light aircraft (see "Der Flug", 10th year, No. 5, page 83) that is built as a biplane. The aircraft costs the currently unmatched low price for a biplane of just 6900 RM, complete with airworthiness certificate, ex works Kassel. With their extremely healthy pricing policy in the aircraft industry, the works are accelerating a development that required decades of work, experience and concentration in the leading automobile industry, which is friendly to the works. The first series of 20 units is even to be sold at the introductory price of just 5900 RM per aircraft.
The technical details are as follows:
Central fuselage between wings, seats one behind the other, dual controls. Biplane, staggered, cantilevered with torsion bars. Engine mounted in the nose of the fuselage on a steel tube foundation with shock absorbers in between, working on a traction propeller. Tail unit and rudder with normal elliptical outline, horizontal stabilizer braced once against the fuselage, rudder unbalanced, ailerons on the upper wing.
Material and design of the fuselage: steel tube frame with tube diagonals in the edges and wire crossovers in the horizontal planes, fabric covering.
Material and design of the wings: normal wooden construction, I-spars, lattice spars, inner posts and wing tips, dural tube, inner bracing, steel wire. Aspect ratio of the wing: 1:7.5 at the top, 1:6.7 at the bottom. Angle of the wings at the top: 0.5°, at the bottom 1.0°. V-position of the wings 0°.
Material and design of the tail unit:
wooden frame, fabric covered. Landing gear and skid: Normal steel tube, landing gear, rubber cord suspension, skid made of duralumin tube.
Crew: One pilot and one passenger or student pilot.
Powerplant: Engine: three-cylinder Anzani, air-cooled; Engine power about 35 hp; Propeller drive: direct; Fuel transport: natural gradient;
Fuel storage: Tank in the upper wing; Fuel capacity: 42 liters.The flight characteristics of the "Grasmücke" are excellent. Above all, the aircraft has a short take-off, good climbing ability and low landing run-out and a high payload. The "Grasmücke" has a weight of only around 250 kg and a payload of around 200 kg and is double-sided to carry a passenger and luggage. The seating arrangement is comfortable and both the pilot and the guest can get in without any difficulty. The engine starts easily. The low weight makes the machine easy to transport.
The aircraft is economical in terms of oil and fuel consumption. You will fly it yourself and, thanks to the strict standardization of the simple design of the airframe and the simplicity of the engine, anyone can carry out any necessary minor manipulations themselves and save on the cost of a mechanic.
The "Grasmücke" is equipped with dual controls. Its excellent flight characteristics, as already mentioned, make it the ideal training aircraft, which above all enables the owner to train private pilots inexpensively. The lower wing is continuous and provides an area of 8x1.2 m for advertising lettering, which, due to its position, is not disturbed by the undercarriage in the advertising effect of the lettering downwards. The D number is placed on the upper wing. The sides of the fuselage are also ideal for advertising lettering. With the ever increasing popularity of aircraft advertising, the "Grasmücke" will find a versatile use in the service of advertising. The Raab-Katzenstein aircraft factory has been producing the vast majority of all advertising aircraft for years. The decisive factor for the success of the "Grasmücke" in all areas of application, in addition to its excellent technical properties, will be its low price of 6900 RM, which the factory will certainly reduce even further as sales increase.
The German aircraft industry once again deserves special credit for being the first to take this path to creating a cheap, everyday aircraft, {according to the Raab-Katzenstein factory.)
R. K. 9 "Grasmücke", light aircraft.
After several months of design and production work, the Raab-Katzenstein aircraft works have brought out a light aircraft which, in contrast to the monoplane type previously used in German light aircraft construction, is built as a biplane. The aircraft costs RM 6900, complete with airworthiness certificate, from the Kassel factory. The first series of 20 units will even be sold at an introductory price of just RM 5900 per aircraft.
As the development of German private and sport aviation has so far been primarily and most strongly hampered by the prohibitively high prices of motor aircraft, the widest circles of our readers will be interested in the new release. This cantilevered, staggered biplane with torsion bars has a simple structure. In the central fuselage between the wings, the seats are located one behind the other with dual controls. The engine is in the nose of the fuselage on Steel tube foundation supported with interposed shock absorbers. The fuselage consists of a steel tube frame with tube diagonals in the edges and wire crossovers in the horizontal planes, fabric covering, tail unit and rudder show a normal elliptical outline, horizontal stabilizer braced once against the fuselage, rudder unbalanced, ailerons on the upper wing. The wings in normal wooden construction have I-spars, lattice spars, inner stems and wing tips made of dural tube, inner bracing made of steel wire. The aspect ratio of the wing is 1:7.5 in at the top, 1:6.7 m at the bottom. Angle of the wings at the top 0.50°, at the bottom 1.0º. V-position of the wings 0°.
The flight characteristics of the Warbler are excellent. Above all, the aircraft has a short takeoff, good climbing ability and low landing run-out and high payload. The Warbler has a weight of just 250 kg and can carry a payload of around 200 kg, and is designed as a two-seater to carry a passenger and luggage.
Engine: 3-cylinder Anzani, 35 hp, air-cooled. Tank: 42 l in the upper wing.
Wingspan: 8.960 m at the top, 8.060 m at the bottom. Length: 6.850 m. Height: 2.300 m. Load-bearing area: 19.64 m2.
Equipped weight: 250 kg. Filling: 200 kg. Full weight: 450 kg. Wing loading: 22.90 kg/m2. Power load: 12.8 kg/hp.
Top speed: 120 km/h. Average speed: 100 km/h. Landing speed: 40 km/h. Flight time with one fuel tank: 4 hours. Operating radius: 400 km. Climb time to 1000 m altitude: 13 min. service ceiling with full load: 3600 m.
The biplane's supporting structure has continuous, cantilevered wooden wings with I-spars and I-spars arranged in rows. Instead of screw bolts for fastening fittings, steel tubes are used, which are beaded on one side at the points of the inner post fastenings and secured against falling out by split pins. The main suspension fittings are attached by tubular rivets. The spar ensures good ventilation of the inside of the wing, which was achieved by numerous recesses in the spar. For the same reason, the box made up of the leading edge, front spar and plywood paneling is directly connected to the inside of the wing. In addition, ventilation eyelets are attached to the fabric covering at the trailing edge of the wings. - To reduce the cost of series production, a constant wing depth, rectangular plan, etc. was chosen. The spar dimensions of both wings, post fittings and wing ribs are also the same. The slightly rounded ends of the wings are formed on the lower wing by aluminum tubes, and on the upper wing by wooden edge arches, in order to have the necessary construction height for the aileron balance. The wing pattern used is Göttingen No. 387.























