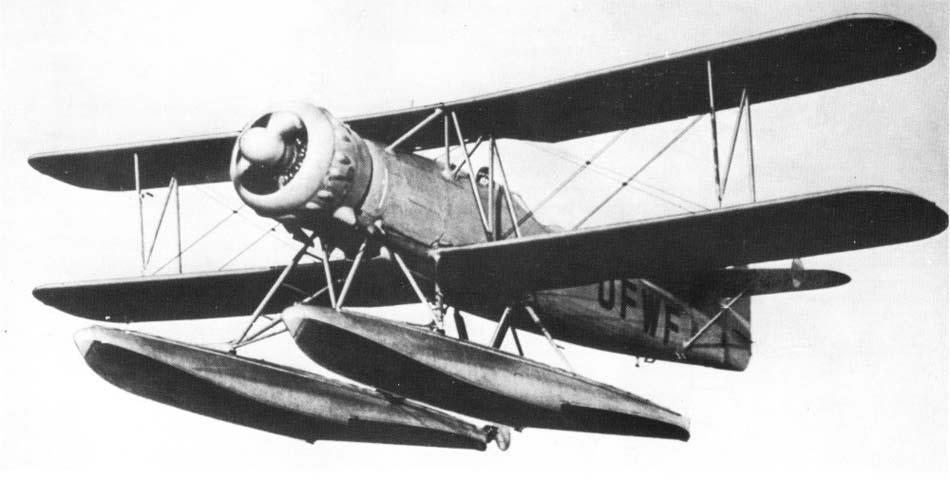
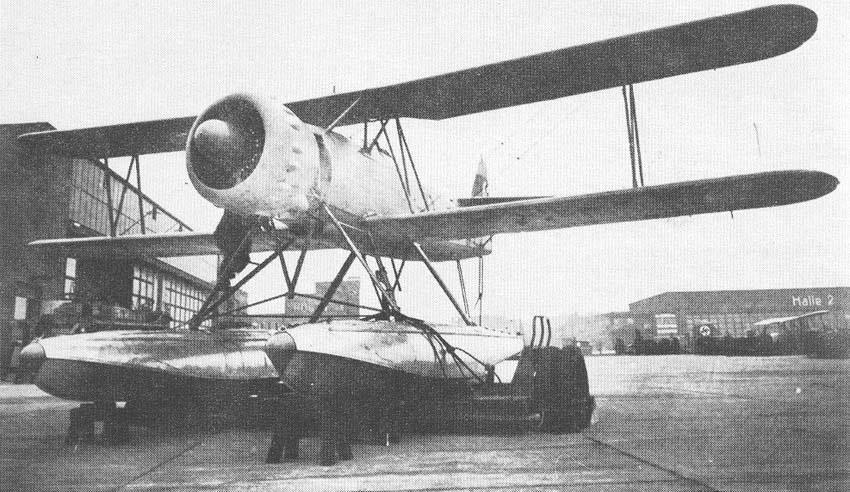
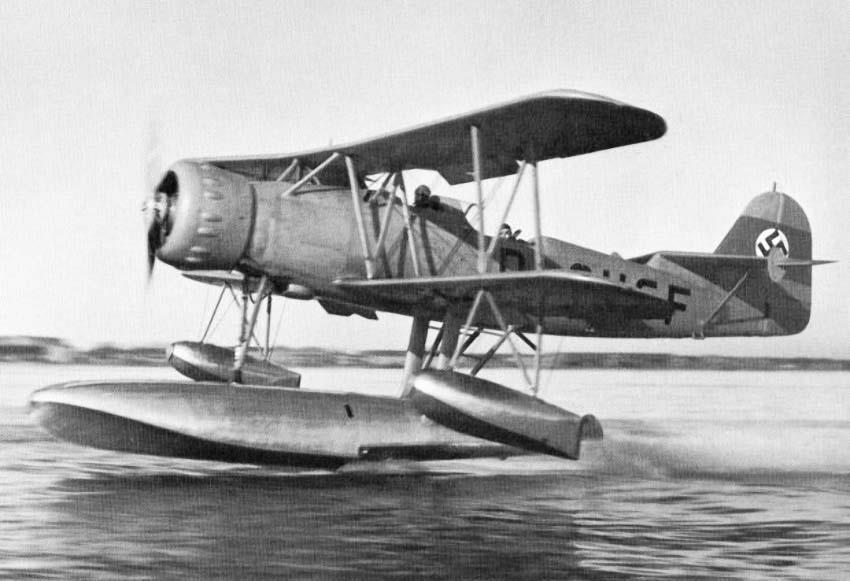
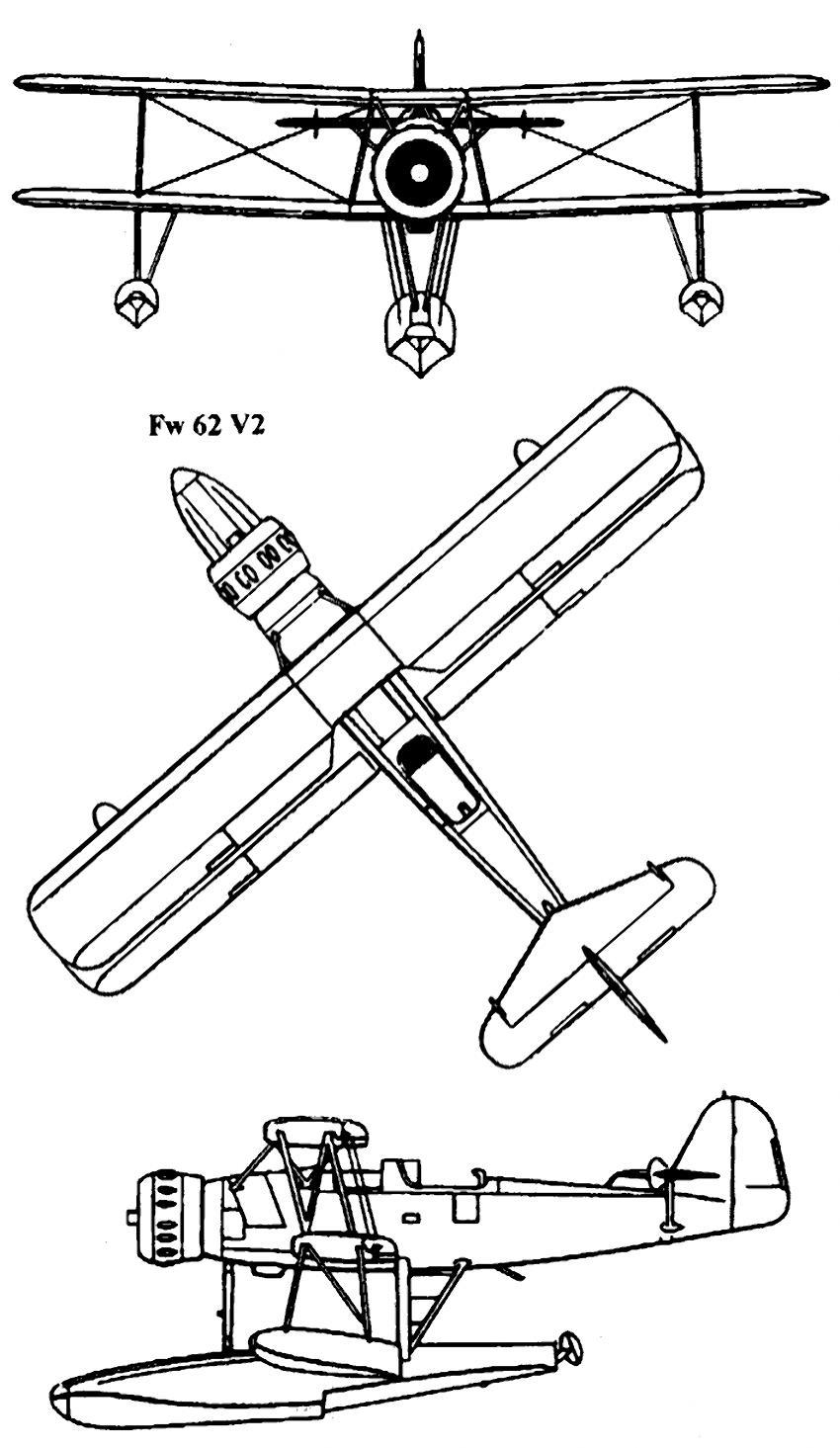
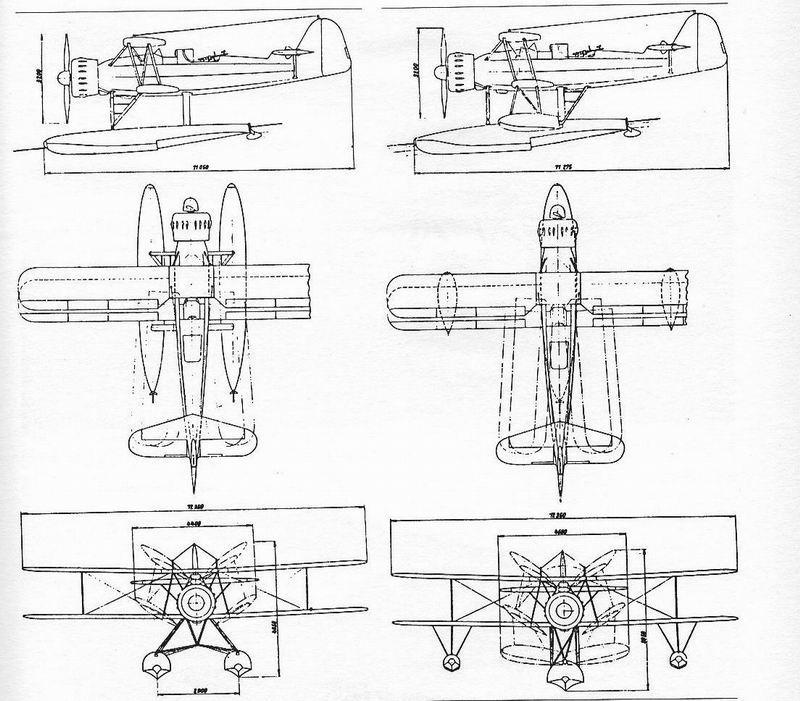
| Type | V1 2-seat reconnaissance floatplane |
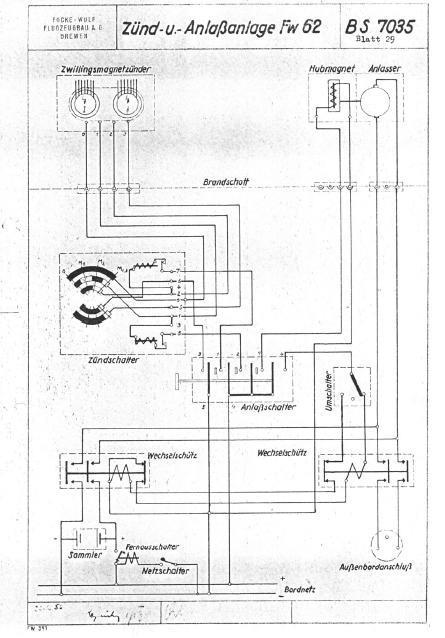
| Engine | 1 BMW 132Dc with 2-bladed controllable-pitch propeller |
| Dimensions | Length 11,15 m, height 4,3 m , span 12,35 m , wing area 36,1 m2 , |
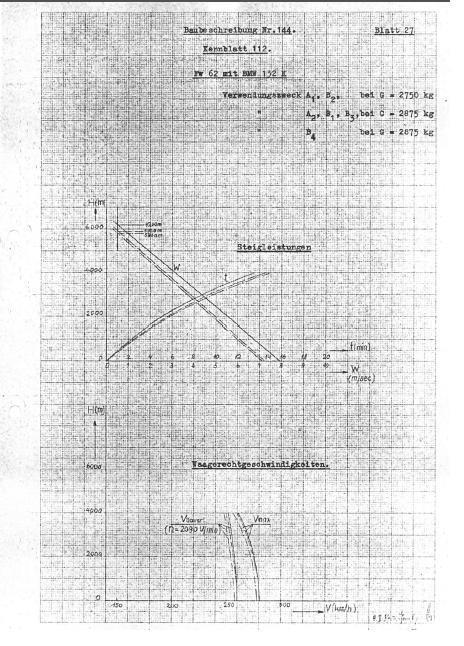
| Weights | Empty 2300 kg, loaded 2850 kg , max. take off weight |
| Performance | Max.. speed 280 km/h at 1000 m, cruising speed 251 km/h , range 900 klm, endurance , service ceiling 5900 m, climb 6,4 m/sec. |
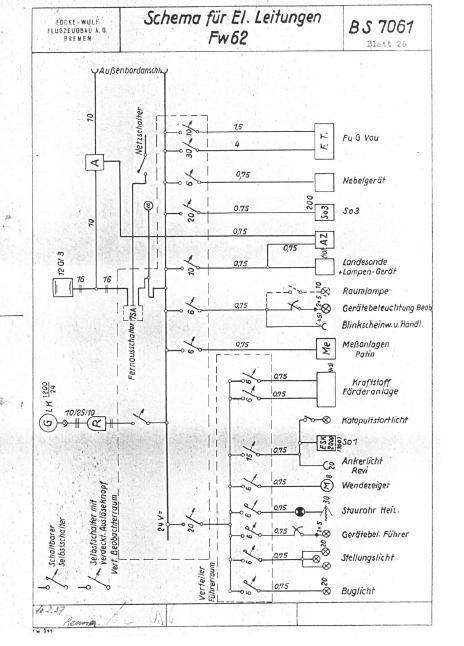
| Armament | 1 7.92 mm MG 15 machine gun in rear cockpit. Bombs: 4 50 kg SC 50 bombs. |
| Type | Werk.Nr | Registration | History |
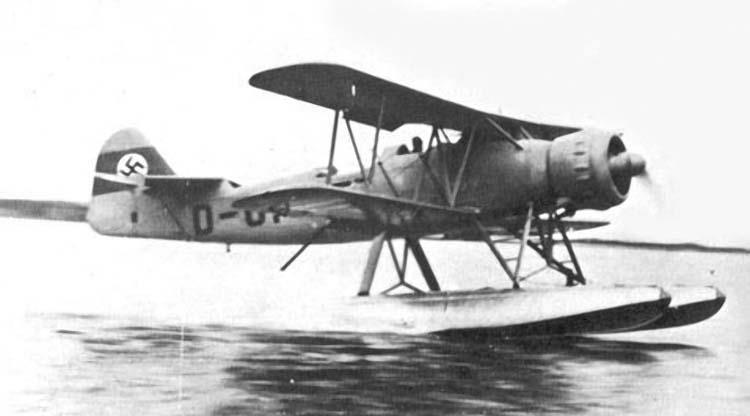
| V1 | 2062 | D-OFWF | First flight January 5, Repair of corrosion damage at the Travemunde test site December 12, 1938 September 26, 1939 Travemunde E-site reports that the machine sank a week earlier while moored at a buoy. Cause: left float filled up due to leaky cross seams in stormy weather. |
| V2 | 2063 | D-OKDU | 3. 1938 Kurt Tank flew it in Travemünde |
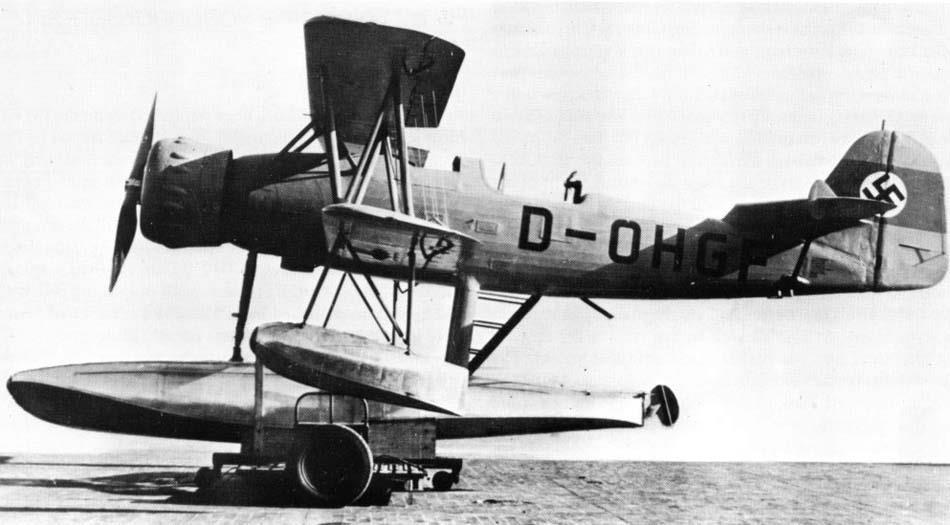
| V3 | 2064 | D-OHGF | 10 January 1938 flown by Kurt Tank in Travemünde (same on 18 January, 22 January and 3 August 1938) 9 January 1938. Airplane crashed during splashdown, badly damaged and sank. 6 January 1939 Repair of central and support floats planned; damage occurred during a sea trial carried out on 25 and 26 May 1939 in List/Sylt by the Institute for Maritime Aviation of the DVL, Hamburg, . V 3 repaired and tests with this aircraft continued |
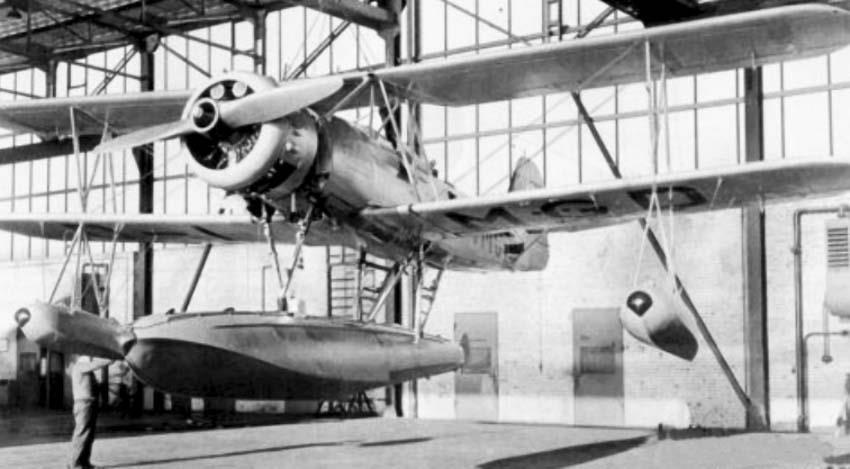
| V4 | 2065 | D-OMCR, former D-IMGD | 1938 The machine is said to have flown by Tank during testing and after delivery in |