The D. P. VIIa is somewhat similar to the D.P.IIa as regards its fuselage, which is of similar construction, but it is a parasol monoplane and hns a five-cylinder Siemens radial engine of 60 h.p. This machine, it may be remembered, was exhibited at the Prague Aero Show last year. The monoplane wing is carried by X-struts. The wing is built in two halves so as to facilitate transport.
| Type |
Two seat trainer |
| Engine |
1 Siemens Sh 6 |
| Dimensions |
Length 6.02 m, height 2.22 m, span 9.66 m, wing area 14.00 m2 aspect ratio 6.65 |
| Weights |
Empty 385 kg, fuel 60 kg, oil 4 kg, load 225 kg, flying weight 610 kg, wing loading 43.6 kg/m2 |
| Performance |
Max. speed 140 km/h, cruising speed 125 km/h, climb 1.85 m/sec, to 1000 m 9 min., service ceiling 3200 m,range 550 km, landing speed 60 km/h, runway for start 60 m, for landing 50 m |
| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
|
|
D-524 |
|
|
144 |
D-530 |
|
|
|
D-531 |
|
|
|
D-633 |
|
|
156 |
D-634 |
|
|
|
D-637 |
|

Dietrich-Gobiet small aircraft D. P. Vila. 55 HP.
The new aircraft from Dietrich-Gobiet-Flugzeugverke A.-Q., Cassel, is intended to be used as a touring or sports aircraft.
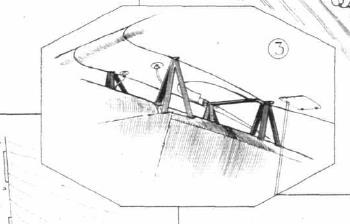
Each half of the two-part high wing is hinged to the tension tower on the one hand and supported against the fuselage by N-struts on the other. The
wing profile is Qöttingen 387 at the connection of the struts and tapers outwards and towards the fuselage. The box spars with spruce spars and plywood webs
are reinforced at the nodes of the inner crossover by locked filler blocks and provided with light webs at the connection points of the spars. The spars, which have
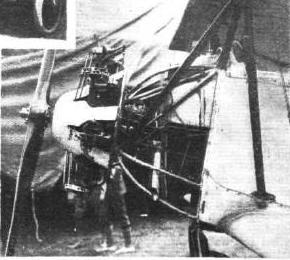
strongly recessed leading edges and plywood caps, run into a finishing strip made of plywood strips glued to spruce strips. The unbalanced ailerons are mounted on the wing tips, the tapered auxiliary spar is heavily recessed and is supported by the lamella-like glued edge arch and the middle box spar. The N-spars are designed in such a way that the angle of inclination can be adjusted at any time. The main supports of the posts consist of round tubes covered in a teardrop shape by wooden cladding, while the diagonal struts are made of teardrop profile tubes. The proven steel tube construction was chosen for the fuselage, and steel tube crosses were chosen to absorb the diagonal tensions in the vertical fuselage walls and steel wire crosses in the horizontal and inner fields. The seats are installed low, so that the occupants are in an almost half-reclining position. The front j-control can be easily removed and can also be switched off from the rear seat using two handles, for example if the aircraft is in a standing position. B. the student sitting in front should work against the teacher's steering movements. Above the front seat, the canopy rests on 12 short, streamlined aluminum sheet clamping tower supports. Easy entry is achieved through a large viewing cutout and a fold-up clamping tower cross brace. Behind the driver's seat, there is a triangular flap in the aluminum paneling that provides access to a removable luggage bag for travel luggage (up to 5 kg). If the easily attached luggage bag is removed, the entire interior of the fuselage can be seen to check the control cables. The control surfaces are welded from tubular steel, the fixed fins can be removed and braced at the top by a drop tube and at the bottom by steel cables in a triangular configuration. The divided elevator and the rudder, coupled in the middle, are unbalanced and mounted in normal brass shells. To attach the M-design chassis to the fuselage, only strong normal bolts subject to pure shear stress are used instead of the ball sockets and bolts that were common in earlier designs, while the M-struts are attached to the auxiliary axle using a wide clamp, which allows a certain tolerance in the slidability of the framework. The chrome-nickel steel axle is suspended in spring-loaded cords, with the spring travel being approx. 120 mm and limited by catch loops. The 170x85 wheels are covered with aluminum disks. ^

High-wing aircraft DP Vila
All of the above projects - with the exception of the DP IX - were designed in 1924. The "Luftford" was built and flown in the same year. It was a year of enormous activity for Dietrich-Gobiet aircraft construction. The DP Vila, a pleasing strutted high-wing aircraft in mixed construction, was also built and flown in 1924. Three of these took part in the first German sightseeing flight in 1925, along with the DP Ila.
However, none of the aircraft built brought any significant progress compared to the DP Ila. The competition with aerodynamically more high-quality aircraft from Klemm and Messerschmitt was also stronger than that of Dietrich.
The DP VIla, which was fully capable of flight in the future, was no more successful than its predecessors. The main focus of Dietrich aircraft construction was still on the DP Ila.