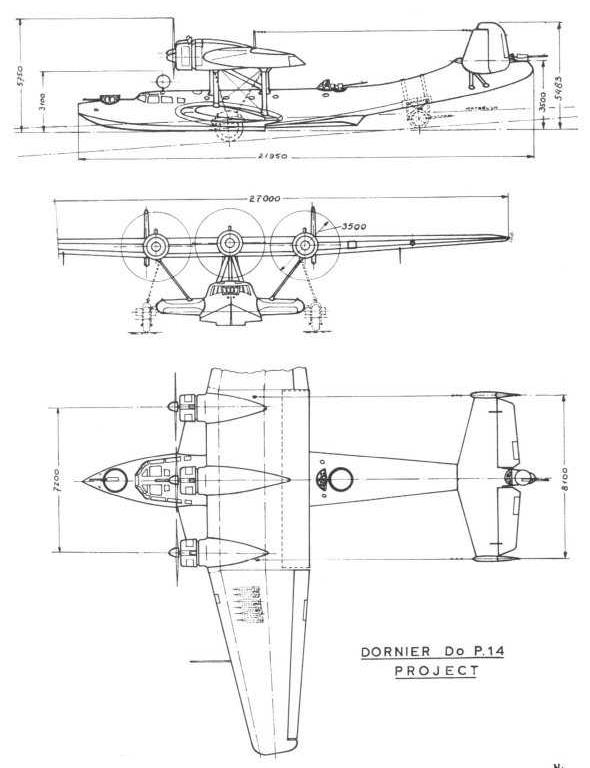
| Type |
|
| Engine |
propellerdia 3,5 m |
| Dimensions |
Length 21,350 m , height 5,465 m , span 27,00 m , wing area , |
| Weights |
Empty , loaded , max. take off weight |
| Performance |
Max.. speed , cruising speed , range , endurance , service ceiling , climb |
| Armament |
|
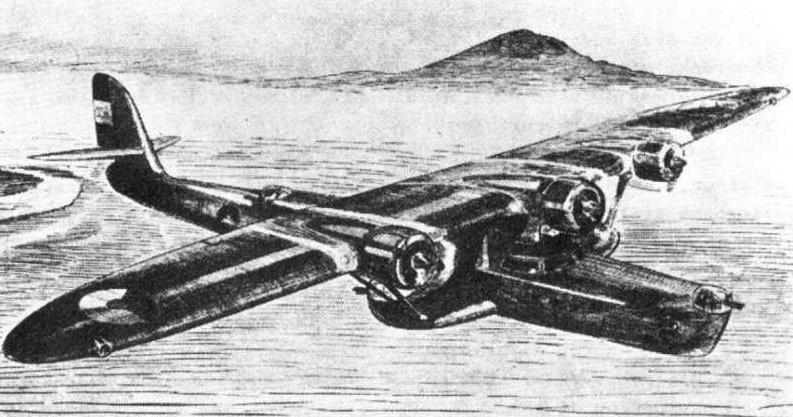
Back in 1926 the Dutch Navy ordered a number of Dornier Wal flying boats to patrol the vasteness of the Dutch Indies, with distanses streching out sometimes more than from one side of Europe to the other. The Wal's performed good, but soon got outdated and in 1934 the Navy started an investigation into a succeeder for the Wal. Around that time Dornier-Metallbauten G.m.b.H. in Friedrichshafen made the first prototype for the Do-18, a modernized version of the Wal. The Do-18 did not meet up to the required standards of the Dutch Navy. C. Sanders, then officer 2nd class of the Navy, made up the requierements of the successor of the Wal. The new plane had to be bigger, equipped with three engines, none of these to use pusher propellers, a maximum speed of 315 km/h, be of an all-metal construction and comforatble enough for long distances.
With these specifications in hand the Dutch Navy went to a number of company's for their answer to the requirements. Fokker came up with the B.V, which was turned down, just like the design of the American Sikorsky company. Dornier's design, the P.14 was ready in 1935 and was the only of the three that could be ready in time to meet the requirements of the Dutch Navy. Before the year was over a detailed model was ready to be shown to the Dutch.
Very soon Dornier was able to make an offer, after which on August 6th 1936 the first contract was signed for the delivery of 6 flying boats to the Dutch Navy, getting the designation Do-24.